Overview
Applications
Comparison

Chemical formula

Specific gravity
1.24
Thermal properties
65
Tg(℃)

160~
Tm(℃)

Characteristics

Biodegradability

Rigidity
Difficult to injection mold

Impact resistance
Commentary
Sugar is extracted from sugarcane, corn, sugar beets, etc., and fermented to produce lactic acid, which is polymerized to form a polymer. It is finally decomposed into water and carbon dioxide by microorganisms in nature.
Key points
- Low decomposition performance compared to other biodegradable plastics, and almost no decomposition unless in a composting environment
- Adjust rigidity by alloying with PBAT, and use as biodegradable mulch film for agriculture
- Difficult to crystallization and need longer cooling temperatures in injection molding

Agricultural mulch film

Reason for adoption
Highly permeable to moisture and acids, degrades in soil after hoeing (biodegradable)
Cutlery

Reason for adoption
Biomass, biodegradable


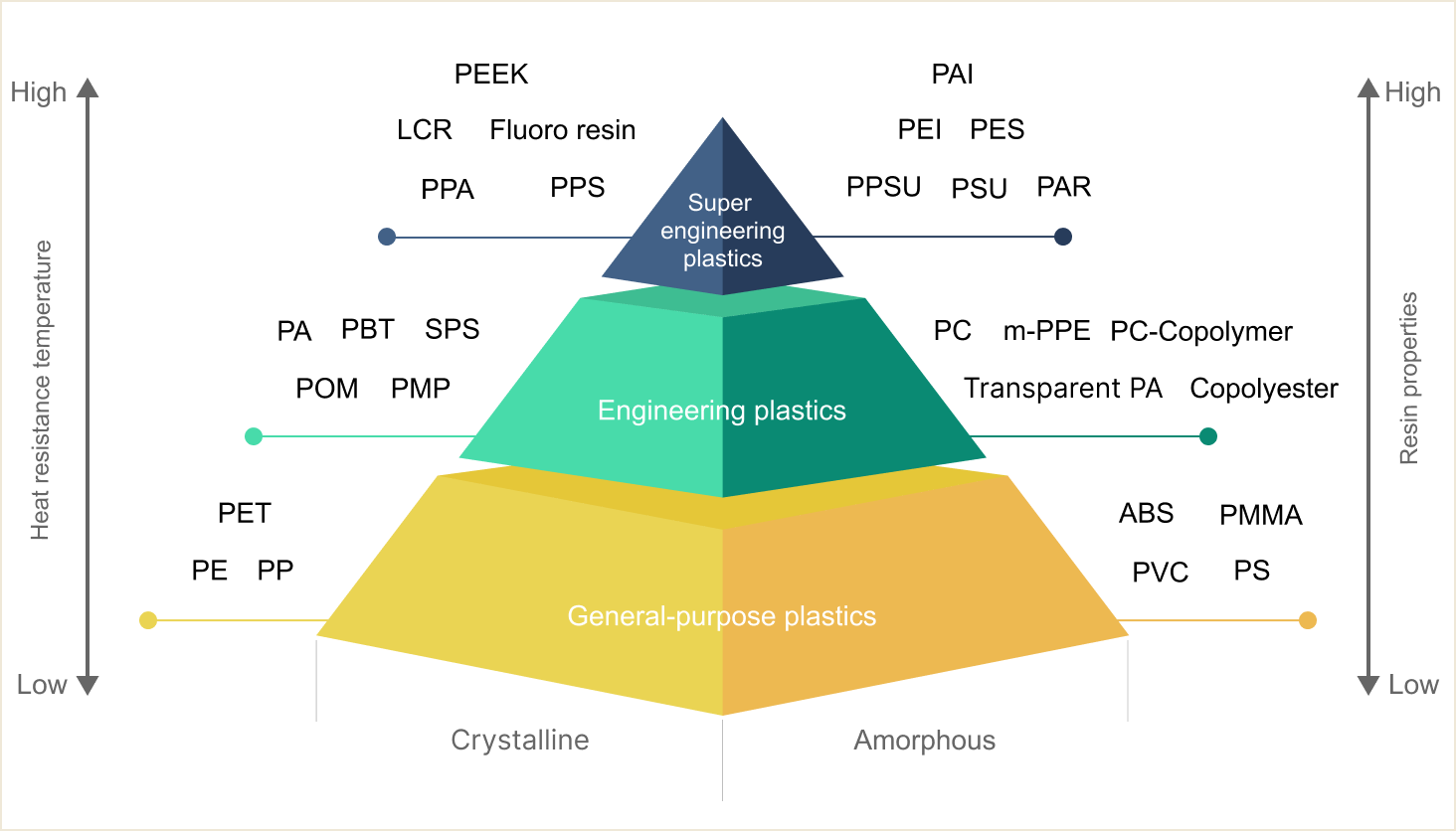
Crystalline

Polyethylene

Polypropylene

Polyethylene
Terephthalate

Polyoxymetylene /
Polyacetal

Polybutylene
Terephthalate

Polyamide 6 /
Polyamide 66

Syndiotactic
Polystyrene

Poly Phenylene Sulfide

Polyphthalamide

Liquid Crystal Polymer

Fluorocarbon Polymers

Polyether-etherketone

Polymethyl-pentene