Overview
Applications
Comparison

Chemical formula

Specific gravity
1.20
Thermal properties
140
Tg(℃)

N/A
Tm(℃)
Characteristics

Impact resistance

Transparency

Flame retardancy

Weatherabilty
Flow ability

Hydrolysis resistance

Scratch resistance
Commentary
The interfacial polymerization method using bisphenol A and phosgene as raw materials has been the mainstream method, but in recent years, ester exchange method (dissolution method), which does not use phosgene, has also been used for production.
Key points
- Transparent and high impact resistance even with thin walls.
- Used in many industrial products due to its excellent heat resistance and flame retardant properties.

Gallon bottle

Reason for adoption
Not breakable when dropped, withstands water pressure (impact resistance, rigidity), visible inside (transparency)
Headlamp Covers

Reason for adoption
Unbreakable even when hit by pebbles, high transparency, lightweight (impact resistance, transparency, weather resistance, low specific gravity (compared to glass))
Carport Roof

Reason for adoption
Good at transparency. weather resistance, lighter than glass ( lower specific gravity)


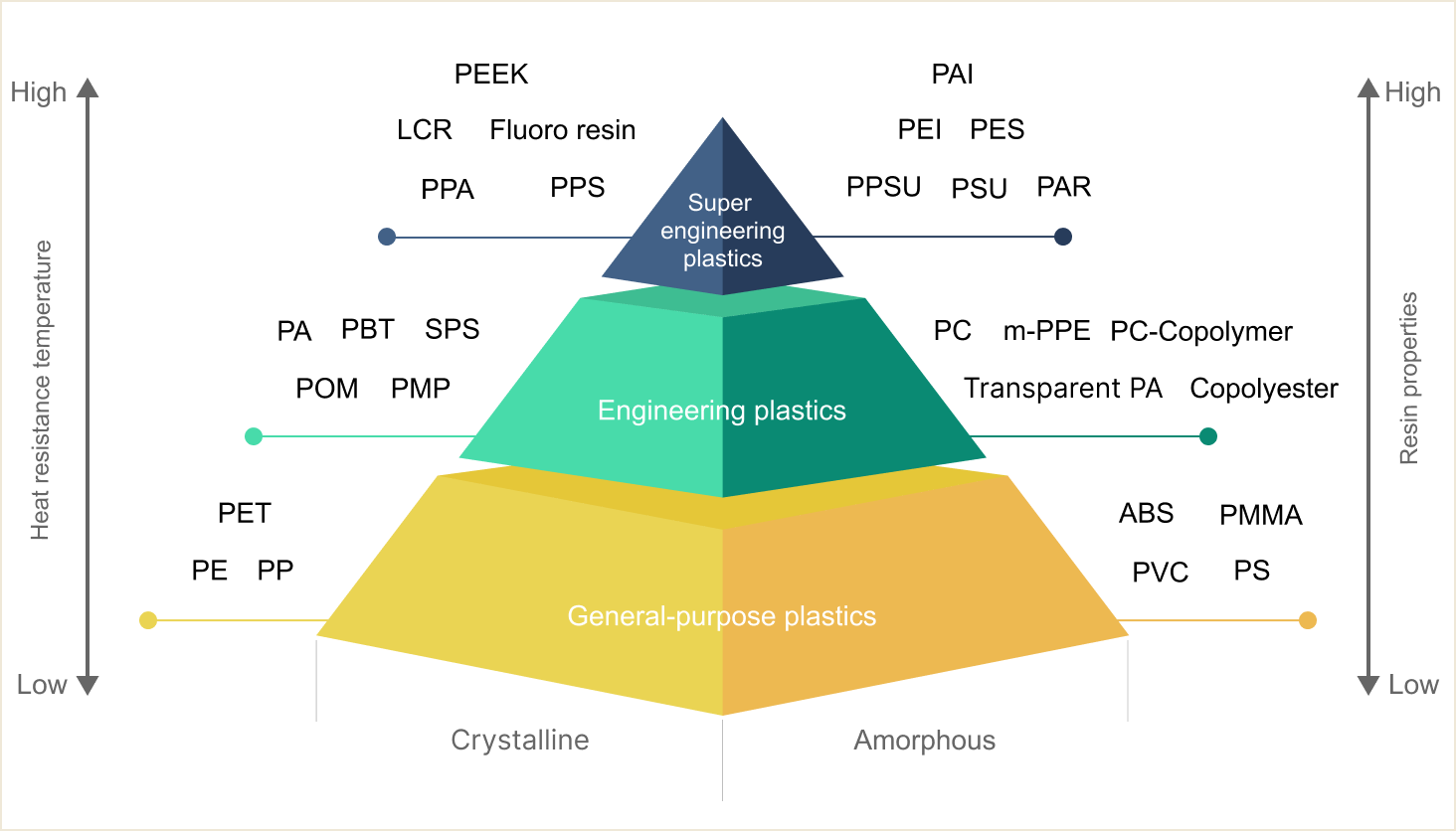
Crystalline

Polyethylene

Polypropylene

Polyethylene
Terephthalate

Polyoxymetylene /
Polyacetal

Polybutylene
Terephthalate

Polyamide 6 /
Polyamide 66

Syndiotactic
Polystyrene

Poly Phenylene Sulfide

Polyphthalamide

Liquid Crystal Polymer

Fluorocarbon Polymers

Polyether-etherketone

Polymethyl-pentene