Overview
Applications
Comparison

Chemical formula

Specific gravity
1.30

Thermal properties
143
Tg(℃)

343
Tm(℃)

Characteristics

Heat resistance

Impact resistance

Mechanical properties

Chemical resistance

Wear resistanse

Radiation resistance

Hydrolysis resistance

Fatigue resistance

Resistance to concentrated sulfuric acid
Commentary
A polymer obtained by nucleophilic substitution reaction ofhydroquinone and4,4-difluorobenzophenone, in which benzene rings are connected by ether and ketone bonds. It has a very low VOC content and is therefore highly pure.
Key points
- There is no molecular weight degradation even at high temperatures/high water vapor levels.
- The continuous use temperature is also high at around 250°C, and the material is self-extinguishing.
- In addition, it resistant to chemicals, radiation, metal ion contamination, and abrasion.
- It can meet the strict requirements of special environments such as the aerospace and semiconductor industries.

Precision brake system components (plungers)

Reason for adoption
Resistant to heat, oil, and slippery (Low coefficient of friction), have good mechanical strength, dimensional stability and sealing properties
Source PressReleaseFinderMedical Tubing

Reason for adoption
Good at sterilization processes, has good flexibility, and has high heat resistance, radiation resistance, chemical resistance, fatigue resistance, etc.
Source www.solvay.comMagnet wire insulation material for electric motors

Reason for adoption
No volatile organic compounds. Provides good adhesion to copper wire in a single layer and can be used to create thick insulation up to 180 microns.
Source PressReleaseFinder

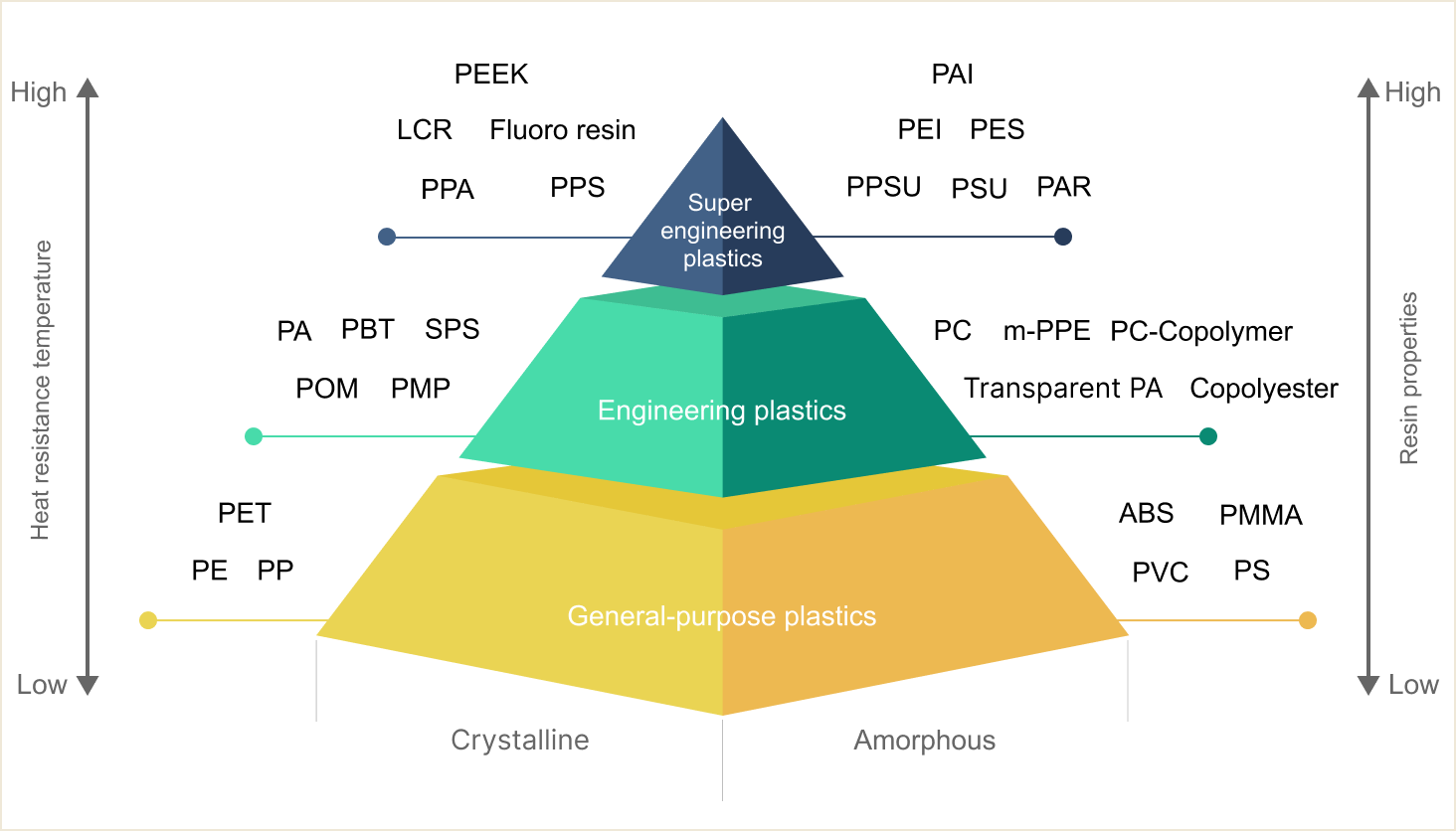
Crystalline

Polyethylene

Polypropylene

Polyethylene
Terephthalate

Polyoxymetylene /
Polyacetal

Polybutylene
Terephthalate

Polyamide 6 /
Polyamide 66

Syndiotactic
Polystyrene

Poly Phenylene Sulfide

Polyphthalamide

Liquid Crystal Polymer

Fluorocarbon Polymers

Polyether-etherketone

Polymethyl-pentene