Overview
Applications
Comparison

Chemical formula

Specific gravity
1.31

Thermal properties
40
Tg(℃)

230
Tm(℃)

Characteristics

Chemical resistance

High Toughness

Heat resistance with GF

Injection moldability

Electrical insulation resistance

No dimensional stability
Commentary
It is synthesized by condensation polymerization of terephthalic acid and 1,4-butanediol. Because it has an ester bond (-COO-) in main chain of polymer, hydrolysis occurs in high temperature and high humidity environments, and its strength decreases.
Key points
- Widely used for electrical and electronic connector applications by high electrical insulation resistance, dimensinal stability and lower water absorption rate than PA.
- Reinforced with glass fiber, it can be used for applications requiring rigidity and heat resistance.
- There is a similar crystalline polyester resin called GF-reinforced PET, which has higher heat resistance than GF-PBT, but PBT is better for injection molding.

Connectors

Reason for adoption
Good at electrical perfomance (electrical insulation resistance, tracking resistance), easy to formulate for flame retardancy, can withstand use at high temperatures (with GF)
Headlight housings

Reason for adoption
Balanced strength, electrical properties, heat resistance, good injection moldability
EV chargers (PBT/PC alloy)

Reason for adoption
Electrical properties, flame retardancy, weather resistance


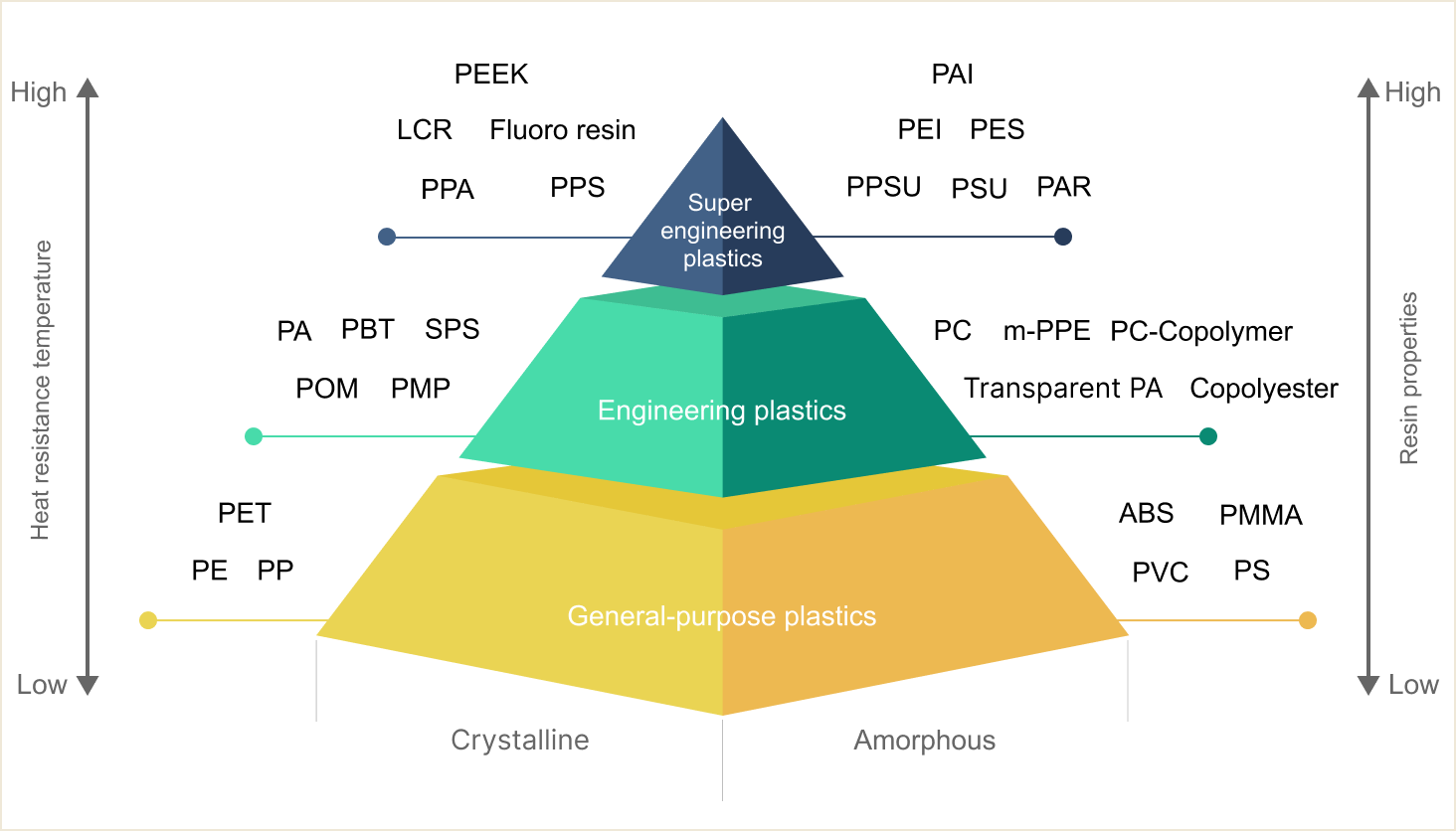
Crystalline

Polyethylene

Polypropylene

Polyethylene
Terephthalate

Polyoxymetylene /
Polyacetal

Polybutylene
Terephthalate

Polyamide 6 /
Polyamide 66

Syndiotactic
Polystyrene

Poly Phenylene Sulfide

Polyphthalamide

Liquid Crystal Polymer

Fluorocarbon Polymers

Polyether-etherketone

Polymethyl-pentene