A Decomposition Solution That Replaces Conventional Adhesive Removers|Solving Disposal and Waste Challenges of Traditional Debonding Agents
“We’re seeing whitening on substrate surfaces,” “The strong odor is causing headaches among workers,” “Disposal drums for used removers are overflowing,”—manufacturing sites and research labs involved in bonding processes are increasingly seeking alternatives to conventional adhesive removers. Particularly, the strong dissolving power of removers based on solvents such as toluene and methyl ethyl ketone poses challenges, including substrate damage, residue contamination, and high disposal costs.
This article outlines the problems with traditional adhesive removers and introduces a novel decomposition solution that addresses these challenges. We hope this information will be helpful to corporate social responsibility officers exploring safer disposal methods and to process engineers aiming for zero adhesive residue in their operations.

Identifying Problems with Traditional Adhesive Removers
Severe Substrate Damage
Conventional organic solvent-based removers eliminate adhesive layers by completely dissolving polymer chains such as epoxy or urethane. As a result, surface oxide layers on substrates such as aluminum or stainless steel may be etched, and stress cracks can form in plastic substrates such as polycarbonate or acrylonitrile butadiene styrene. In microscopic inspections, mirror-finished surfaces (Ra 0.05 µm) have been observed to roughen beyond 0.5 µm, significantly reducing yield rates in optical and precision components.
Residue Contamination
Epoxy adhesives form a robust 3D cross-linked network, reaching molecular weights in the millions once cured. When softened by traditional removers, fillers (e.g., silica) tend to aggregate, often leaving behind a cloudy gel-like residue on the substrate surface. This residue can compromise adhesion in downstream processes such as re-bonding, repainting, or wire bonding, requiring additional steps such as solvent cleaning, polishing, and degreasing.
Costly Waste Disposal
Used removal liquids contain large amounts of adhesives, pigments, fillers, and oils, making them highly viscous and heterogeneous. With distillation recovery rates as low as 30%, the residue-laden distillate is typically incinerated as industrial waste. Additionally, solvents such as toluene and xylene fall under fire safety regulations, requiring permits or explosion-proof storage for certain volumes. The entire lifecycle—from use to storage and disposal—incurs substantial costs and labor, underscoring the need to re-evaluate how adhesive removers are used and discarded.
Exploring Decomposition Solutions as an Alternative
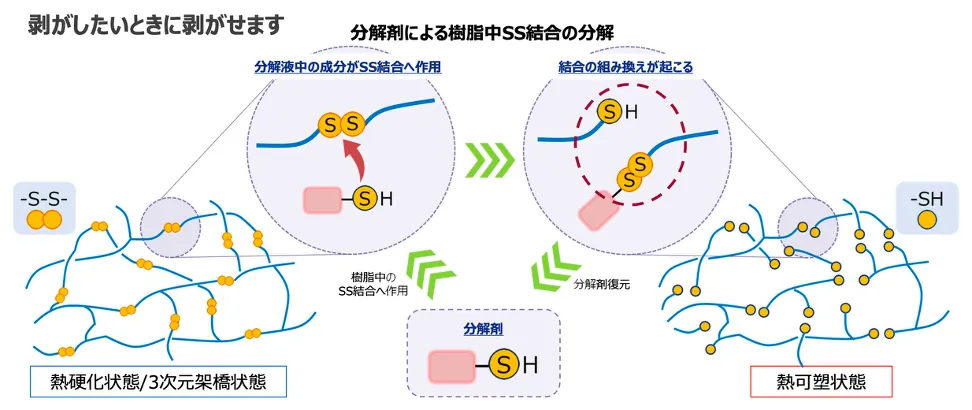
A new alternative technology—easily debondable adhesives—incorporates disulfide (S-S) bonds into the epoxy resin backbone, enabling both high strength under normal conditions and selective cleavage in the decomposition liquid. The specially designed decomposition solution is neutral and combines reducing agents with polar solvents to precisely break only the S-S bonds.
Minimizes Substrate Damage
This solution operates under mild conditions—below 60℃—effectively preventing damage to adherends. It also supports ambient temperature handling, greatly improving operator safety and working conditions.
Leaves No Residue, Enables Complete Removal
By selectively cleaving S-S bonds, the cross-linked polymer network is rapidly reduced to low molecular weight fragments. This untangling mechanism allows full dissolution of cured resin (e.g., 100 mg sample) within 24 hours at 25℃ or four hours at 60℃, leaving no traces of fillers or pigments. When used with ultrasonic cleaning, takt time can be further reduced by 30%, and adhesive removal is achieved without the need for polishing or detergents.
Enables Recycling
The debonded resin reverts to a thermoplastic state via the reduction reaction, making re-molding possible through reheating. Both the resin and the solvent can be reused in a closed-loop process. This approach helps achieve a triple win by reducing raw material procurement, minimizing industrial waste disposal costs, and lowering Scope 3 CO₂ emissions.
Using Easily Debondable Adhesives That Detach on Demand
Developed by Nagase ChemteX, easily debondable adhesives deliver high bonding performance under normal conditions yet can be cleanly and safely removed under mild conditions using a special decomposition solution—with no harsh chemical solvents. They minimize substrate damage and enhance part recyclability. The decomposition liquid itself is reusable, contributing to environmental sustainability.

These adhesives incorporate reversible disulfide (S-S) bonds into the epoxy network. When immersed in the dedicated solution at ambient temperature below 60°C, these bonds are selectively cleaved, breaking down the molecular chains and dissolving the adhesive.
Key Features
Additional Benefits
- ●Safety: Easily Debondable Adhesives are halogen-free, non-toxic, and solvent-free formulation minimizes workplace risk.
- ●Multi-Material Compatibility: Enables clean separation of metal, resin, and composite interfaces.
- ●Circular Use: Reusable decomposition liquid significantly reduces disposal costs.
- ●Mass Production Ready: Jig-free batch processing (immersion → rinse → dry), suited for applications such as EV battery modules and building materials.
For more information on decomposition mechanisms, available product grades, or operational guidance, please refer to the product introduction page.