Decomposition Liquids as Alternatives to Adhesive Remover Solutions
Adhesive remover solutions have long been used in manufacturing and maintenance settings to remove strongly bonded adhesives without damaging the base materials or finished products. However, conventional removers still pose challenges, including high volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, thermal substrate deformation from heating, long immersion times, and even surface dissolution of the base material.
This article summarizes the issues associated with traditional adhesive remover liquids and introduces the promising alternative technology of easily debondable adhesives, which address these limitations. The article provides engineers seeking more functional and eco-friendly solutions with a detailed explanation of key considerations and benefits for implementation.

Problems with Conventional Adhesive Remover Solutions
Environmental Issues: VOC Emissions During Disposal
Most conventional adhesive remover solutions are based on petroleum-derived organic solvents such as toluene, methyl ethyl ketone (MEK), and acetone. Due to their high volatility, these solvents easily evaporate at ambient temperature and contribute to environmental problems such as photochemical smog and unpleasant odors. Protective ventilation systems and gas masks are essential to mitigate inhalation risks during use, leading to increased capital and operational costs. Moreover, when the spent solvents are incinerated as industrial waste, both disposal costs and CO₂ emissions are unavoidable.
In response, regulations such as the EU VOC Emission Directive and Japan’s Pollutant Release and Transfer Register system demand a shift to low-VOC products and tighter emissions control. Transitioning to environmentally friendly alternatives is becoming urgent. When reducing VOCs, it is important to quantify content in accordance with standards such as ISO 11890-2:2020. Presenting objective data on compliance and reduction performance strengthens a company’s environmental reporting and customer audit outcomes.
Often Disposed of Without Recycling
Used adhesive removers often contain solid residues such as resin fragments, fillers, and pigments, making them difficult to recycle. While partial solvent recovery through distillation is possible, it consumes significant energy, and many sites opt for incineration instead.
The lack of solvent recycling results in CO₂ emissions throughout the solvent’s life cycle—from production and transport to disposal—posing challenges in the context of decarbonization and circular economy goals. Life cycle assessments (LCAs) increasingly highlight the environmental burden of such practices, and this has become a point of review in corporate sustainability efforts.
Recently, low-cost options such as leased or modular solvent recovery systems (e.g., vacuum thin-film distillers) have become more accessible, encouraging small and mid-sized coating or adhesive plants to engage in recycling efforts.
Incomplete Decomposition Leaves Residues Behind
High-strength adhesives such as epoxy and cyanoacrylate types possess chemically stable three-dimensional crosslinked networks, making complete breakdown difficult with traditional solvents. As a result, gel-like residues may remain on the surface, leading to poor adhesion, coating failure, or interface defects in subsequent processes.
In fields that demand sub-micron cleanliness—such as semiconductor manufacturing and precision optics—these residues can cause critical contamination. Additional processes such as plasma cleaning or laser ablation may be required, extending production takt time and increasing costs.
To ensure residue-free cleaning, both the choice of decomposition liquid and optimization of cleaning methods—such as ultrasonic agitation, low-pressure spray flow, or vacuum immersion—are critical. In fact, decomposition tanks with built-in ultrasonic transducers have been shown to improve penetration through cavitation and shorten cycle times by 30–40%. Optimizing both chemistry and process can improve equipment efficiency and yield.
Introducing Decomposition Liquid as a Substitute for Adhesive Removers
Nagase ChemteX’s “easily debondable adhesive” (ET-071 series) incorporates disulfide (SS) bonds into the epoxy resin backbone. This allows the adhesive to maintain strong bonding under normal conditions, while transforming into a thermoplastic state when immersed in a dedicated decomposition liquid. This “selective breakdown only when needed” structure enables processing under mild conditions (25–60℃), lowering the barrier for use on production lines.
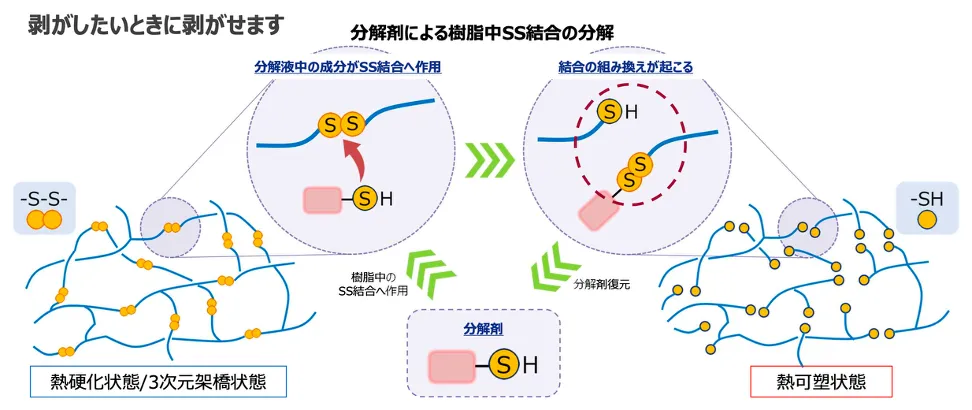
Complete Adhesive Removal Without Residue
In tests where 100 mg of cured adhesive was stirred in 3 g of decomposition liquid, complete dissolution occurred in 24 hours at 25℃ and in 4 hours at 60℃. No resin particles or whitening residues were observed on the substrate surface. Moreover, the solution can dissolve up to 20 wt% resin (1 g resin per 5 g solution), making it suitable for cleaning large components.
Recyclable
The product is designed to leverage the reversible reaction of SS bond cleavage and reformation, enabling the separated resin to be thermoplastically reused. The decomposition liquid is also low-viscosity (1.3–1.8 mPa·s), making distillation-based recovery feasible. This supports a closed-loop recycling system for both adhesive and solvent.
Minimal Damage to Substrates
The ET-071 series offers two grades: a single-phase system (WO-002) and a two-phase system (oil layer WO-003 / water layer WW-003). Both have excellent penetration and achieve complete reaction with mild stirring at 60℃and 300 rpm. The system avoids the need for high-temperature firing or strong solvents, allowing safe use with metals, carbon fiber-reinforced polymer, and optical resins. Although some discoloration (yellow to brown) may occur, it does not affect performance.
Easily Debondable Adhesives That Peel Only When Required
Developed by Nagase ChemteX, easily debondable adhesives deliver high bonding performance under normal conditions yet can be cleanly and safely removed under mild conditions using a special decomposition solution—with no harsh chemical solvents. They minimize substrate damage and enhance part recyclability. The decomposition liquid itself is reusable, contributing to environmental sustainability.

These adhesives incorporate reversible disulfide (S-S) bonds into the epoxy network. When immersed in the dedicated solution at ambient temperature below 60°C, these bonds are selectively cleaved, breaking down the molecular chains and dissolving the adhesive.
Key Features
Additional Benefits
- ●Safety: Easily Debondable Adhesives are halogen-free, non-toxic, and solvent-free formulation minimizes workplace risk.
- ●Multi-Material Compatibility: Enables clean separation of metal, resin, and composite interfaces.
- ●Circular Use: Reusable decomposition liquid significantly reduces disposal costs.
- ●Mass Production Ready: Jig-free batch processing (immersion → rinse → dry), suited for applications such as EV battery modules and building materials.
For more information on decomposition mechanisms, available product grades, or operational guidance, please refer to the product introduction page.