Adhesion Promoter "DENACOL" for Improving Coating Adhesion
DENACOL, A Coating Adhesion Promoter
Here we introduce "DENACOL," developed over many years by Nagase ChemteX Corporation.
What is DENACOL?
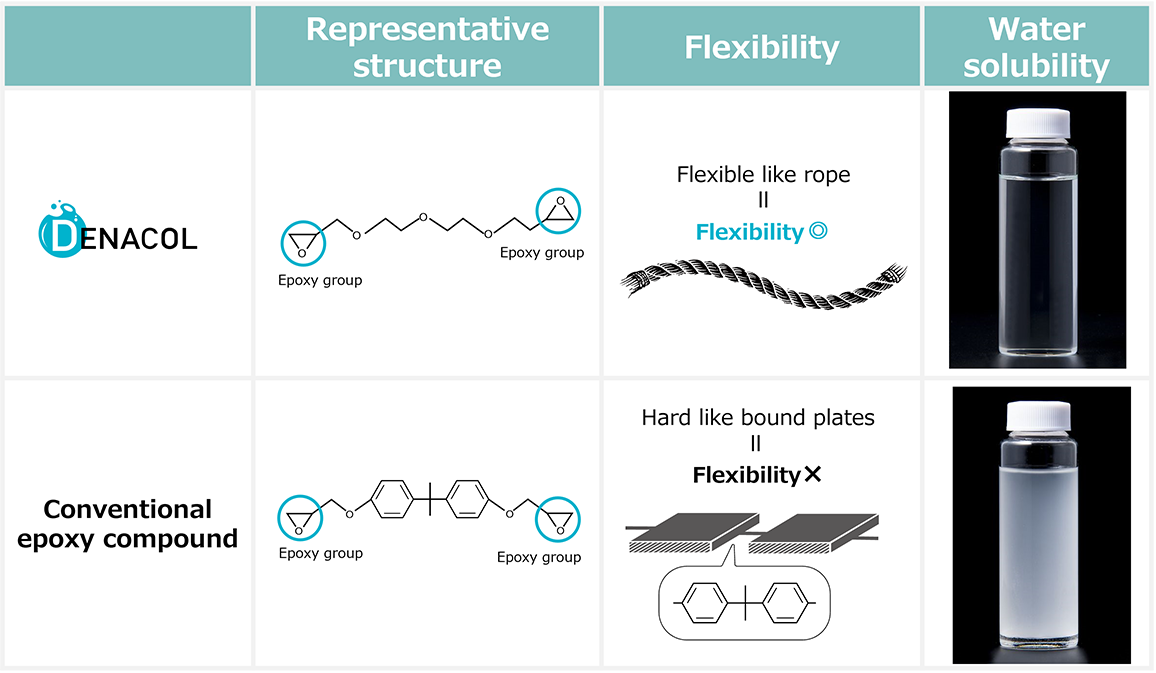
DENACOL is an epoxy compound formed by glycidyl etherification (or esterification) of alcohol hydroxyl groups and carboxylic acids. It is suitable as a coating adhesion promoter.
As it contains epoxy groups as functional groups, it functions as a crosslinking agent, delivering significant adhesion improvement.
Features of DENACOL
DENACOL has several features:
- Flexibility
- Weather resistance
- Water solubility
- Low environmental impact
- Diverse product lineup
Flexibility refers to the property of bending or flexing without breaking when subjected to external force. Weather resistance means the ability to withstand natural environmental conditions such as UV rays.
Since DENACOL is water-soluble, it can be used in water treatment applications. It also dissolves easily in solvents. Being VOC-free, it has minimal environmental impact and can be used in various environments.
DENACOL Types
DENACOL products are broadly classified into five types, catering to various applications:
● Multifunctional type:High reactivity and durability
● Difunctional type:Suitable for applications requiring mild crosslinking structures
● Monofunctional type:Includes a variety of aliphatic and aromatic epoxies
● Low-chlorine type:Reduced chlorine content
● Green DENACOL:Bio-based epoxy compounds derived from plants
Recommended Grades for Improving Coating Adhesion
Among the diverse lineup, four recommended grades belonging to the multifunctional type are introduced below. These are characterized by water solubility, high reactivity, and low viscosity, and are used as crosslinking agents for water-based paints and adhesives, as well as surface treatment agents for fibers.
EX-313
Chemical name: Glycerol polyglycidyl ether
Table 1. Specifications of EX-313
| Epoxy equivalent(g/eq.) | Viscosity (mPa・s) |
Total chlorine content(%) | Color Value (APHA) | Water solubility(%) | Packaging |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 141 | 150 | 9 | 10 | 99 | 20kg, 220kg |
EX-421
Chemical name: Diglycerol polyglycidyl ether
Table 2. Specifications of EX-421
| Epoxy equivalent(g/eq.) | Viscosity (mPa・s) |
Total chlorine content(%) | Color Value (Gardner) | Water solubility(%) | Packaging |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 159 | 650 | 9.6 | 1 | 88 | 20kg, 220kg |
EX-614B
Chemical name: Sorbitol polyglycidyl ether
Table 3. Specifications of EX-614B
| Epoxy equivalent(g/eq.) | Viscosity (mPa・s) |
Total chlorine content(%) | Color Value (Gardner) | Water solubility(%) | Packaging |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 173 | 5,000 | 10.1 | 3 | 94 | 20kg, 220kg |
EX-512
Chemical name: Polyglycerol polyglycidyl ether
Table 4. Specifications of EX-512
| Epoxy equivalent(g/eq.) | Viscosity (mPa・s) |
Total chlorine content(%) | Color Value (Gardner) | Water solubility(%) | Packaging |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 168 | 1,300 | 6.5 | 40 | 100 | 20kg, 220kg |
What is a Coating Adhesion Promoter?
Coatings are applied to the surface of materials or components (hereafter referred to as substrates) to improve their performance. They serve multiple purposes, such as enhancing hardness to prevent surface scratches or improving weather resistance to protect against UV rays and sea air.
However, if the coating does not adhere properly to the substrate, these effects cannot be fully realized. To ensure proper adhesion, adhesion promoters are used.
Factors That Affect Adhesion
There are multiple methods to improve adhesion. This article introduces the use of crosslinking agents as adhesion promoters.
For example, the combination of water-based resins that contain functional groups, such as carboxyl groups, with adhesion promoters that contain epoxy groups forms a crosslinked structure through an addition reaction. A crosslinked structure refers to the state where individual polymers are bonded, which not only enhances adhesion but also improves the overall hardness and durability of the coating layer. This allows the coating to perform its functions more effectively.
Applications of Coating Adhesion Promoters
Coating adhesion promoters are used in a variety of applications. Representative examples are introduced below.
Floor Coating
Floor materials are susceptible to scratches due to heavy foot traffic or the placement of office equipment and fixtures. For this reason, floor coatings are applied to protect the surface.
By using adhesion promoters to bond the coating to the flooring material, surface protection performance improves. Certain types of adhesion promoters can also reduce volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions, thereby minimizing their impact on indoor environments.

Marine Coating
Boats and Ships
Since the majority of a ship’s hull is submerged underwater, it requires high durability to withstand such conditions. Adhesion promoters strengthen the bond between the coating and the hull, providing durability in marine environments. Additionally, it is essential that adhesion promoters do not harm the natural environment. In some cases, bio-based adhesion promoters derived from plants are used.

3C Coating
Electronics, Computers, Consumer Electronics
3C refers to electronics (communication devices), computers (computers), and consumer electronics (customer electronics). Since electronics include smartphones, these are all items frequently used in our daily lives.
Because 3C products are often handled directly, coatings are applied to protect them from dirt and scratches. Using adhesion promoters ensures strong adhesion, allowing the coating to perform its functions effectively.
Comparison of Adhesion Promoters
There are various types of adhesion promoters. Below are some representative examples.
Crosslinking Agents
Crosslinking agents are additives that bond polymer compounds (polymers) to create a crosslinked structure. By using crosslinking agents, polymer chains are chemically bonded or interact with each other, improving adhesion and hardness. They are also used to enhance both solvent and heat resistance.
Different types of crosslinking agents are chosen based on the desired functional group (the starting point of the crosslinking reaction), such as carboxyl, hydroxyl, or amino groups.

Silane Coupling Agents
Coupling agents are compounds with both an organic reactive site and an inorganic reactive site. Silane coupling agents, which contain silane, are examples of this. They possess functional groups called alkoxy groups, which react with substrates like metal, glass, and film, functioning as coupling agents.

Inquiries and Sample Requests
For more information or sample requests, please feel free to contact us.

