NAD/NADH Assay Kit-WST
NAD/NADH Assay Kit-WST
細胞内の代謝システムである、回答系やTCA回路、ペントース-リン酸経路の解析は、細胞状態を理解するうえで重要であり、グルコースや乳酸、NAD(P)*/NAD(P)Hなどのエネルギーおよび代謝産物を指標に評価されています。
Product information
細胞内代謝測定(NAD⁺/NADH)
Principle
NAD/NADH Assay Kit-WST enables quantification of the amount of total NAD+/NADH, NADH and NAD+ in cells and measurement of their ratio.
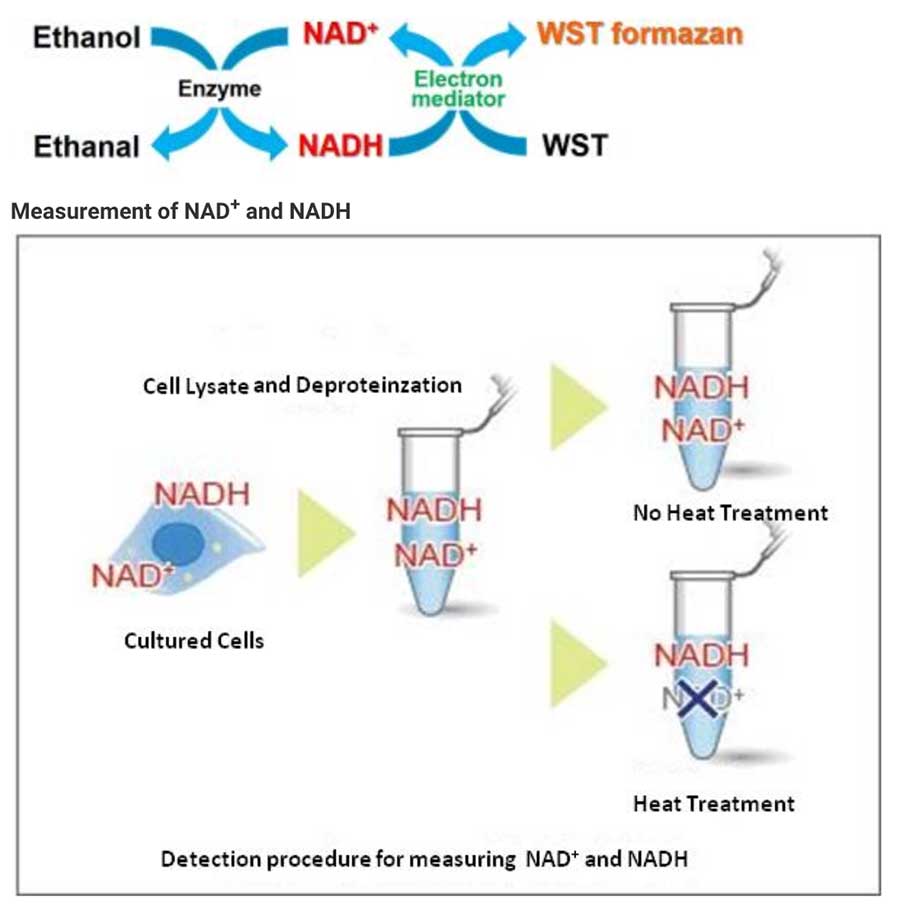
Cell lysate from a cell culture can be easily prepared via Deproteinzation using the extraction buffer and filtration tubes found within this kit. Intracellular NADH levels can be quantified by heat treatment of cell lysate. Additionally, intracellular NAD+levels can be determined by subtracting NADH levels from independently measured total NAD+/NADH levels.
Technical info
Recently, it has become clear that Sirtuin is linked to longevity and plays a role in NAD+ level regulation. Also Sirtuin has been recognized as a marker necessary to understanding biological states, such as obesity & diabetes, as well as cellular differentiation.

In the experiment shown below, the NAD+ /NADH levels & ratio were determined using HeLa cells.
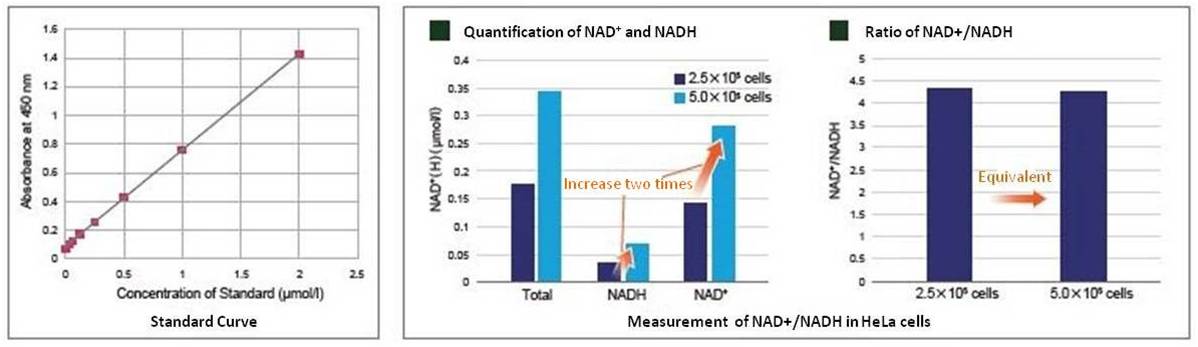
Standard curves were constructed using different concentrations of HeLa cells (2.5×105 and 5.0×105 cells) cultured in growth media. The standard curves were then used to determine the intracellular NAD+ and NADH levels. As a result, NAD+ and NADH levels varied depending on cell number while the change in cell number had no effect on the NAD+/NADH ratio.
Measurement of NAD+/NADH in Combination with Lactate Assay Kit
Change in metabolic activity was observed when the glycolytic inhibitor 2-Deoxy-D-glucose was added to HeLa cells.
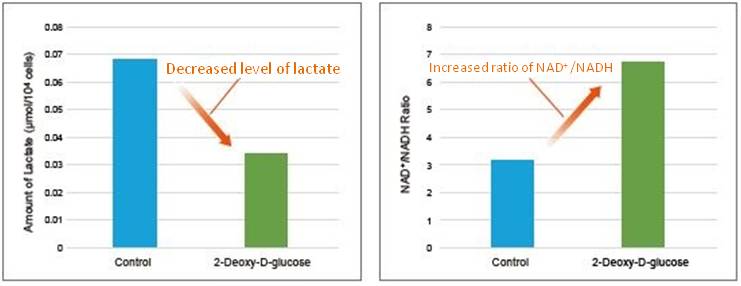
2-Deoxy-D-glucose was added to HeLa cells (1×106 cells) to obtain a final concentration of 6 mmol/l 2-Deoxy-D-glucose. After 24 hours of incubation, lactate levels in the supernatant were quantified using the Lactate Assay Kit-WST (Item#: L256), and the NAD+/NADH ratio was determined with the cell pellet after removing the supernatant using the NAD/NADH Assay Kit-WST.
As a result, intracellular glycolysis was inhibited by 2-Deoxy-D-glucose, which led to decreased lactate levels and an increase in the NAD+/NADH ratio.
Experimental Example: Change in Metabolism in Liver Tissue of NASH-Induced Mouse
It is known that non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) results in decreased ATP, α-ketoglutarate (α-KG), and NAD levels in affected tissues. ATP, α-KG, and NAD levels were measured in the liver tissue of type 1 diabetic model mice (STAM model) that were treated with a high-fat diet (NASH induction) since 4 weeks old. Measurement at 10 weeks old confirmed that ATP, α-KG, and NAD levels indeed decreased in the tissue samples after NASH induction.
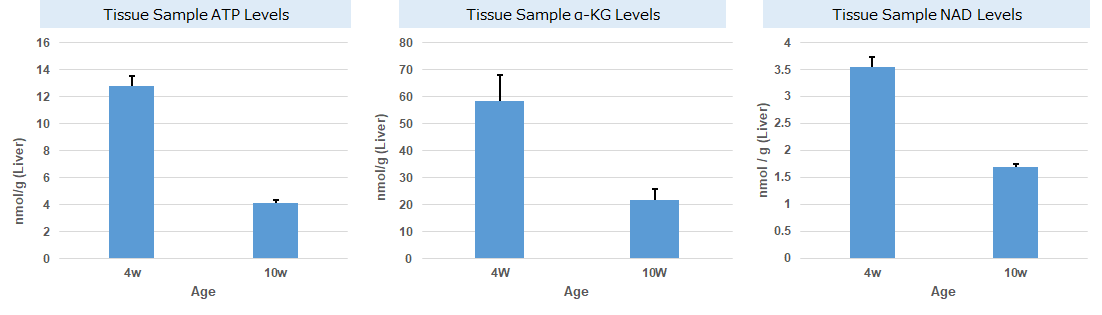
Note: for more details about the experimental procedure, please refer to Q&A "Are there any examples of experiments using tissue samples?"
・Cellular ATP: ATP Assay Kit-Luminescence (Code:A550)
・Cellular α-KG: α-Ketoglutarate Assay Kit-Fluorometric (Code:K261)
・Cellular NAD: NAD/NADH Assay Kit-WST (Code:N509)
References:
ATP
Francesco Bellanti, et al., "Synergistic interaction of fatty acids and oxysterols impairs mitochondrial function and limits liver adaptation during nafld progression", Redox Biology, 2018, 15, 86-96.
α-KG
Jianjian Zhao, et al., "The mechanism and role of intracellular α-ketoglutarate reduction in hepatic stellate cell activation", Bioscience Reports, 2020, 40, (3).
Ali Canbay, et al., "L‑Ornithine L‑Aspartate (LOLA) as a Novel Approach for Therapy of Non‑alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease", Drugs, 2019, 79, 39-44.
NAD
Jinhan He, et al., "Activation of the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Sensitizes Mice to Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis by Deactivating Mitochondrial Sirtuin Deacetylase Sirt3", Mol. and Cell. Biol., 2013, 33, (10), 2047-55.
References
2. S. Mandziuk, R. Gieroba, A. Korga, W. Matysiak, B. Jodlowska-Jedrych, F. Burdan, E. Poleszak, M. Kowalczyk, L. Grzycka-Kowalczyk, E. Korobowicz, A. Jozefczyk and J. Dudka, “The differential effects of green tea on dose- dependent doxorubicin toxicity.”, Food Nutr Res., 2015, 59, 29754.