Basics of Epoxy Flexibilizer | Effects, Usage, Examples, and More
What Is a Flexibilizer?
Flexibilizers are compounding agents that add toughness to hard and brittle resin products. Toughness indicates tenacity. Toughness makes the product more resistant to breakage; conversely, if the product is not tenacious, it will break easily upon impact, like glass. It is used to prevent paint from cracking as it cures and to relieve stresses on the adhesive. Other uses include adding flexibility to hard materials and improving fluidity during molding.
Resin products are composed of raw materials called polymers and compounding agents to adjust mechanical properties. Flexibilizers are one of these compounding agents that add flexibility, impact resistance, and toughness to hard and brittle resins, making them suitable for a variety of uses in modern society.
Effects of Flexibilizers
Improved flexibility
 Because resin has a lighter specific gravity than metal, it is actively used in such structures as airplanes and automobiles to reduce weight, and it is now required to be as strong as metal. Simply making the resin harder to increase its strength will make it brittle and destroy it at the slightest deformation. Therefore, a certain degree of flexibility is necessary to achieve both hardness and strength. Flexibilizers are blended into the resin in certain proportions to reduce hardness and add toughness, making it suitable for structural applications. Flexibility is a necessary element not only for structures but also for fiber materials and adhesives, and flexibilizers are used in various fields.
Because resin has a lighter specific gravity than metal, it is actively used in such structures as airplanes and automobiles to reduce weight, and it is now required to be as strong as metal. Simply making the resin harder to increase its strength will make it brittle and destroy it at the slightest deformation. Therefore, a certain degree of flexibility is necessary to achieve both hardness and strength. Flexibilizers are blended into the resin in certain proportions to reduce hardness and add toughness, making it suitable for structural applications. Flexibility is a necessary element not only for structures but also for fiber materials and adhesives, and flexibilizers are used in various fields.
Improved impact resistance
Providing flexibility also improves impact resistance. This is because flexibility is necessary to absorb shock, allowing the material to change its own shape to some extent. Without flexibility, i.e., without toughness, the material will crack and break without being able to change its shape in response to external impact. The addition of a flexibility-imparting material can address this problem.
Improved toughness
Toughness allows a material to deform under force while preventing fracture and to return to its original shape when force is applied. The opposite of toughness is brittleness, which refers to the phenomenon of fracture without much deformation. The addition of a flexibilizer allows the material to deform like rubber and prevent cracking. The addition of toughness also makes cutting possible.
Role of Flexibilizers
Flexibilizers are composed of carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen linked by single bonds and are characterized by the ability to stretch and shrink like rubber. On the other hand, hard resins, such as thermosetting resins, are hard and brittle because the polymers are connected by a hardener. The role of a flexibilizer is to connect the hardeners with soft rubber to change the material so that it does not crack even if it is deformed.
Usage
Electronic materials
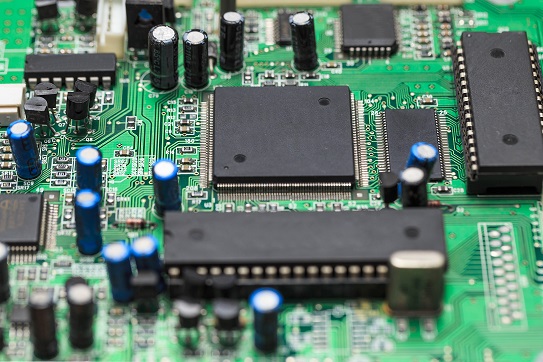 With the recent developments in IT technology, electronic components are required to have high heat resistance and low dielectric properties to support large capacity and high-speed communication. They are also required to be flexible so that they will not be destroyed when subjected to vibration, as is the case in automobiles. To achieve all of these requirements, it is necessary to add suitable compounding agents. Therefore, flexibilizers are used to combine flexibility with other functions.
With the recent developments in IT technology, electronic components are required to have high heat resistance and low dielectric properties to support large capacity and high-speed communication. They are also required to be flexible so that they will not be destroyed when subjected to vibration, as is the case in automobiles. To achieve all of these requirements, it is necessary to add suitable compounding agents. Therefore, flexibilizers are used to combine flexibility with other functions.
Plastic parts
 The compounding agents that provide flexibility are generally small-molecule substances called plasticizers. There are two types of plastic materials: thermoplastics, which soften when heated and harden when cooled, and thermosetting resins, which harden when heated and cause a chemical reaction. Thermoplastic resins have the property of deforming when heated, while thermosetting resins, once cured, do not deform when heated. All types of resins may contain plasticizers to improve fluidity when molding. Flexibilizers are used as plasticizers.
The compounding agents that provide flexibility are generally small-molecule substances called plasticizers. There are two types of plastic materials: thermoplastics, which soften when heated and harden when cooled, and thermosetting resins, which harden when heated and cause a chemical reaction. Thermoplastic resins have the property of deforming when heated, while thermosetting resins, once cured, do not deform when heated. All types of resins may contain plasticizers to improve fluidity when molding. Flexibilizers are used as plasticizers.
Epoxy resins
 Epoxy resin is a generic term for compounds that possess two or more highly reactive three-membered ring epoxy groups in one molecule. By adding a hardener to the epoxy groups, they react to form a hard resin. Epoxy resins have excellent mechanical strength, heat resistance, electrical properties, chemical resistance, and adhesiveness. They are widely used for coating, electrical, and adhesive purposes and in civil engineering. Epoxy resins are also used in printed circuit board laminates and are widely used in electronic and electrical applications. However, general epoxy resins are hard but brittle, and they are weak against impact, so they can be used in a variety of applications by adding flexibilizers.
Epoxy resin is a generic term for compounds that possess two or more highly reactive three-membered ring epoxy groups in one molecule. By adding a hardener to the epoxy groups, they react to form a hard resin. Epoxy resins have excellent mechanical strength, heat resistance, electrical properties, chemical resistance, and adhesiveness. They are widely used for coating, electrical, and adhesive purposes and in civil engineering. Epoxy resins are also used in printed circuit board laminates and are widely used in electronic and electrical applications. However, general epoxy resins are hard but brittle, and they are weak against impact, so they can be used in a variety of applications by adding flexibilizers.
Typical Examples of Flexibilizers
Here are some typical organic compounds used as flexibilizers.
Ester diol
Ester is one of the names of functional groups of organic compounds and can be obtained by dehydration–condensation of carboxylic acids and alcohols. Polyesters are resins with ester functional groups (COO) and are used in fibers, PET bottles, and paints. A functional group is an atom or group of atoms in an organic compound with a specific structure that is responsible for the compound’s characteristic reactivity.
A compound with two hydroxy groups (-OH) attached to the carbon chain is called glycol or diol. A carbon chain is a compound consisting of many carbon atoms bonded together in a chain. A compound with a hydroxy group attached to the carbon chain is called an alcohol, while a compound with two hydroxy groups is called a glycol or a diol. An ester diol is an organic compound with an ester functional group and two hydroxy groups.
Urethane diol
Urethane is a compound in which an amino group reacts with an alcohol group via a carbonyl group to form a new covalent bond between the nitrogen of the amine and the carbon of the carbonyl group. Polyurethanes are thermosetting resins with urethane bonds.
Polycarbonate diol is a polyol (polyhydric alcohol) used as a raw material for polyurethane. By using polycarbonate diol, polyurethanes with superior water resistance, chemical resistance, and durability can be obtained compared to polyether polyol and polyester polyol. This material is ideal for synthetic leather, thermoplastic resins, paint, and other fields requiring high functionality.
The addition of a flexibilizer to a two-component, urethane-cured structural adhesive provides stress-relaxation properties to the adhesive’s coating film, relieving stresses in the adhesive caused by differences in linear expansion coefficients when dissimilar materials are bonded together.
Polyethylene glycol diglycidyl ether
Polyethylene (PE) is polymerized ethylene and is the most widely produced plastic material in the world. It is used in supermarket shopping bags, buckets, and plastic kerosene tanks. Polyethylene glycol diglycidyl ether (PEGDGE) is a glycidyl etherified (esterified) compound of polyethylene glycol. It is easily hydrolyzed in an aqueous solution, producing a hydroxyl group by ring cleavage.
Product Lineups
Flexibilizers
Nagase ChemteX flexibilizers are bifunctional epoxies that are mainly used in adhesives that require gentle cross-linking. Its low viscosity allows it to be diluted effectively, and it is also used in paints and coatings that use high-viscosity materials.
DNEACOL EX-991L
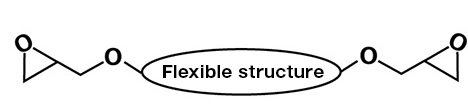 DENACOL EX-991L is insoluble in water, low-chlorine, and, flexible. It is used as a cross-linking agent and flexibilizer for resins used in electronic materials.
DENACOL EX-991L is insoluble in water, low-chlorine, and, flexible. It is used as a cross-linking agent and flexibilizer for resins used in electronic materials.
DENACOL EX-861
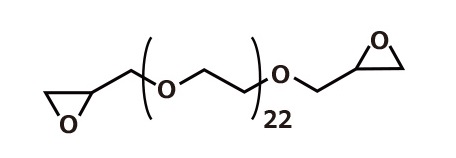 The chemical name of DENACOL EX-861 is polyethylene glycol diglycidyl ether, a bifunctional aliphatic epoxy. It has low viscosity and high water solubility. It is used as a cross-linking agent for water-based resins and as a hydrophilic and flexibilizer. It is soluble in organic solvents as well as water and can be used in both water- and solvent-based systems.
The chemical name of DENACOL EX-861 is polyethylene glycol diglycidyl ether, a bifunctional aliphatic epoxy. It has low viscosity and high water solubility. It is used as a cross-linking agent for water-based resins and as a hydrophilic and flexibilizer. It is soluble in organic solvents as well as water and can be used in both water- and solvent-based systems.
Contact Us
DENACOL, a flexibilizer added to epoxy resins, can be used to control cross-link density, hydrophilicity, and flexibility by selecting hydrophilicity, plasticity, and chain length. Please contact us if you have any questions about improving the function of resins, including flexibility.

