Epoxy Resins for 3D Printers
Epoxy resins are widely utilized as 3D printer materials due to their excellent properties.
This section focuses on DENACOL series and explains the characteristics and applications of epoxy resins, as well as key considerations when using them for 3D printing.
Table of contents
- Epoxy Resins for 3D Printers - DENACOL
- Where Epoxy Resins Are Used in 3D Printing Processes
- Why Engineers Choose Epoxy Resins
- Comparison of Epoxy and Other 3D Printing Materials
- Optimal Epoxy Grade Selection Checklist
- Conclusion
Epoxy Resins for 3D Printers - DENACOL
DENACOL series combines low shrinkage with high reactivity, making it widely adopted as a 3D printer material.
Key Features
We offer an extensive lineup of epoxy compounds that includes both water-soluble and hydrophobic types. These products are VOC-free, contributing to reduced environmental impact. Their excellent epoxy group reactivity makes them suitable for various applications in both aqueous and solvent-based systems, allowing customers to select the optimal product for their specific requirements.
For 3D printing applications in particular, their high dimensional stability and rapid curing properties enable the production of high-precision printed objects.
Recommended Grades
For 3D printing, it is important to select the optimal epoxy resin based on the desired physical properties and processing requirements.
EX-252
This epoxy resin is primarily composed of hydrogenated bisphenol A diglycidyl ether.
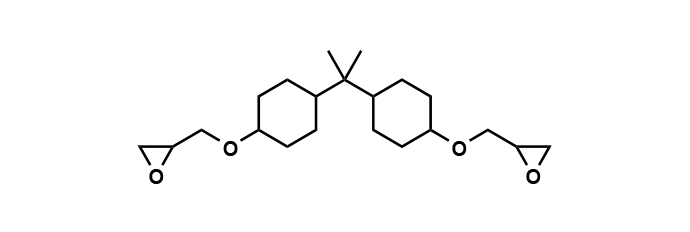
Compared to conventional bisphenol A-type resins, it offers low viscosity for easy handling and excellent flowability in stereolithography printers.
Additionally, it prevents yellowing during the curing process in UV curing systems.
GEX-252
This hydrogenated bisphenol A diglycidyl ether epoxy resin is made from plant-derived raw materials and contains 32% USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) certified bio-based content.

While delivering physical properties equivalent to EX-252, it serves as an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional petroleum-derived epoxy resins. It features low viscosity and excellent flowability, with confirmed improvements in mechanical properties.
EX-614B
This epoxy resin is primarily composed of sorbitol polyglycidyl ether.
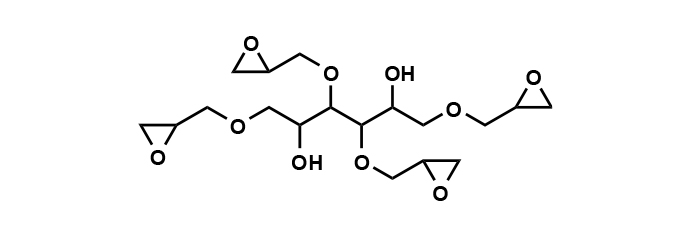
It combines high crosslink density with rapid curing properties to achieve excellent mechanical strength and dimensional stability.
Additionally, it offers outstanding chemical and heat resistance, delivering stable performance even under harsh environmental conditions. Being water-soluble and VOC-free, it can be easily incorporated into aqueous systems.
GEX-614B
This epoxy resin is manufactured from corn and palm oil-derived materials and contains 80% USDA-certified bio-based content.

Like EX-614B, it combines high crosslink density with rapid curing properties to deliver excellent mechanical strength and dimensional stability. It also provides superior chemical and heat resistance, maintaining stable performance even under harsh environmental conditions. This VOC-free, water-soluble epoxy is compatible with amines, acid-functional acrylic resins, and non-isocyanate curing agents.
Its high reactivity and crosslinking density enable the production of high-strength, dimensionally stable 3D printed objects while reducing environmental impact.
Where Epoxy Resins Are Used in 3D Printing Processes
Epoxy resins are utilized in various stages of 3D printing processes due to their excellent properties.
Photopolymer Vat Material
A photopolymer vat is a container that holds liquid resin (photopolymer) which cures under ultraviolet light, and is used in SLA, DLP, and LCD 3D printers.
These methods cure the resin layer by layer using 405nm UV light to build objects. While conventional acrylate-based resins exhibit 5-7% volumetric shrinkage, epoxy resins have low shrinkage rates of less than 2%, reducing warping and deformation to achieve high dimensional accuracy.
Post-Processing Coating and Impregnation
Depending on the printing method, surface defects such as layer lines or voids may occur, affecting both mechanical strength and appearance.
Epoxy resins, with their excellent impregnation and curing characteristics, are widely utilized as post-processing materials. By applying them through coating, immersion, or vacuum impregnation to parts printed using FDM or SLS methods, voids can be filled and surfaces smoothed.
Continuous Fiber Matrix (Niche Applications)
Continuous fiber 3D printing involves impregnating carbon fiber with epoxy resin, depositing it layer by layer with a print head, and curing it through heat treatment.
However, challenges including high equipment costs, slow printing speeds, and geometric constraints limit its use primarily to research and development or specialized applications. Adoption in the aerospace and automotive industries shows promise.
Why Engineers Choose Epoxy Resins
Epoxy resins possess properties that meet the stringent requirements of engineers. Here, we explain the technical reasons why many engineers select epoxy resins as 3D printing materials.
Dimensional Accuracy and Shrinkage Control
One of the primary reasons epoxy resins are chosen as 3D printing materials is their dimensional accuracy. While conventional acrylate-based resins exhibit curing shrinkage of approximately 5%, epoxy resins can limit volumetric change to less than 2%.
| Resin Type | Curing Shrinkage Rate | Dimensional Stability |
|---|---|---|
| Epoxy Resin | 0.1~2% | ◎ |
| Unsaturated Polyester | 7~9% | × |
| Acrylic (MMA) | 5%~ | × |
Superior Mechanical and Thermal Performance
By combining UV curing with thermal curing, epoxy resins can achieve excellent mechanical and thermal properties: flexural strength exceeding 40 MPa and glass transition temperatures (Tg) above 120℃. This performance is comparable to that of engineering plastics used in injection molding.
Chemical Resistance and Formulation Flexibility
The three-dimensional crosslinked network structure of epoxy resins forms a chemically stable framework, providing excellent resistance to various chemicals. They exhibit particularly high resistance to industrial chemicals such as fuel oils, lubricants, and mildly acidic solutions, showing minimal degradation or swelling even after prolonged exposure.
Additionally, they can be formulated with diluents or bio-based resins to meet diverse requirements such as viscosity adjustment or achieving zero VOC content.
Comparison of Epoxy and Other 3D Printing Materials
When selecting 3D printing materials, it is important to understand the advantages of epoxy resins correctly.
Acrylate Resins
Acrylate resins are materials widely used in stereolithography 3D printers and are frequently compared to epoxy resins. They cure within seconds under UV light, offering faster build speeds than epoxy, along with superior productivity and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for prototyping and tooling applications.
However, they have high volumetric shrinkage rates, leading to dimensional accuracy challenges, and become brittle and impact-sensitive after curing. Additionally, their poor resistance to organic solvents restricts their operating environments.
Urethane/Elastomer Systems
These are used for applications requiring flexibility and elasticity, offering excellent shock absorption and extensibility. However, these materials soften at approximately 80℃ and are susceptible to softening and deformation under high-temperature conditions.
Their chemical resistance is moderate when compared to epoxy resins. Being prone to hydrolysis, they require careful consideration for long-term use in high-temperature, high-humidity environments.
Thermoplastic Filaments
These are the most widely used materials in FDM 3D printers.
PLA, a representative material, exhibits relatively low shrinkage and warping during printing, making it suitable for beginners and educational applications. However, PLA has poor heat resistance, with a heat deflection temperature (HDT) of approximately 60℃, making it unsuitable for high-temperature environments.
ABS filament offers superior mechanical strength and impact resistance, making it suitable for a wide range of applications including consumer products and automotive components. However, like PLA, ABS has a heat deflection temperature of approximately 60–80℃, and prolonged exposure to high-temperature environments can cause deformation and strength degradation.
Epoxy's Balanced Performance
Epoxy resins exhibit extremely low curing shrinkage, typically less than 2%, which minimizes warping and deformation even for components requiring precise dimensional accuracy. Additionally, their characteristic three-dimensional crosslinked network provides excellent mechanical strength along with superior heat and chemical resistance.
This makes epoxy resins ideal for applications demanding strict requirements for dimensional accuracy and structural integrity, such as in the automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries.
Optimal Epoxy Grade Selection Checklist
Printer Compatibility
When evaluating printer compatibility for epoxy resins, confirming viscosity and color (appearance) is critical. For stable printing performance, low-viscosity resins below 1 Pa·s are preferred, as high viscosity can negatively impact precision and surface quality.
For transparent components or optical applications, it is essential to select resins with minimal yellowing tendency and excellent transparency and color clarity.
Curing Strategy
- Speed-focused: UV curing (for prototyping and rapid prototyping applications)
- Precision and strength-focused: UV + thermal curing (for functional components)
Performance Targets and Regulatory Compliance
Evaluation criteria include flexural modulus (stiffness), elongation at break (toughness), and glass transition temperature (heat resistance). Furthermore, compliance with environmental regulations such as EU REACH and VOC requirements is essential.
Conclusion
The evolution of 3D printing technology continues to increase the importance of epoxy resins. DENACOL series presented here combines low shrinkage with high reactivity, making it an ideal material for 3D printing applications that demand dimensional accuracy and mechanical strength.
When selecting the optimal resin, considerations must include printer compatibility, curing methods, performance objectives, and environmental regulatory compliance. Given these factors, epoxy resins are expected to see expanded utilization as versatile materials capable of supporting applications from prototyping to mass production, including the manufacturing of high-value-added components.
Inquiries and Sample Requests
For more information or sample requests, please feel free to contact us.
Inquiry / Sample request


