PURINE NUCLEOSIDE PHOSPHORYLASE [PNPLⅡ]
from Bacillus sp.
(Purine–nucleoside: orthophosphate ribosyltransferase, EC 2.4.2.1)
Inosine + Pi → Hypoxanthine + D–Ribose 1–phosphate
Preparation and Specification
- Appearance
- : Colorless to light brownish solution
- Specific activity
- : More than 500 U/ml
Properties
- Molecular weight
- : 280±5 kDa (gel filtration)
36±5 kDa (SDS–PAGE)
- Isoelectric point
- : pH 5.3±0.2
- Optimum pH
- : 8.0Figure 1
- pH stability
- : 6.0–10.0 (37℃, 60 min) Figure 2
- Optimum temperature
- : 65℃ (Tris–HCl buffer) Figure 3
- Thermal stability
- : Stable at 65℃ and below (pH 8.5, 10 min) Figure 4
- Effect of metal ions
- : See Table 1
Applications for Diagnostic Test
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of inorganic phosphate when coupled with xanthine dehydrogenase (T–134) .
| PNPL Ⅱ | ||
| Pi + Inosine | → | Hypoxanthine + Ribose 1-phosphate |
| XDH Ⅱ | ||
| Hypoxanthine + 2 NAD++ H2O | → | Urate + 2 NADH + 2 H+ |
Table 1. Effect of metal ions on PNPL Ⅱ activity
| Metal ion | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|
| None | 100 |
| KCl (10mM) | 107 |
| NaCl (10mM) | 107 |
| CsCl (10mM) | 105 |
| LiCl (10mM) | 107 |
| NH4Cl (10mM) | 107 |
| MgCl2 (1mM) | 107 |
| CaCl2 (1mM) | 101 |
| BaCl2 (1mM) | 105 |
| MnCl2 (1mM) | 36.0 |
| ZnCl2 (1mM) | 102 |
| CoCl2 (1mM) | 24.0 |
| CuCl2 (1mM) | 1.0 |
| NiCl2 (1mM) | 86.0 |
| EDTA (1mM) | 112 |
Fig.1 pH Optimum
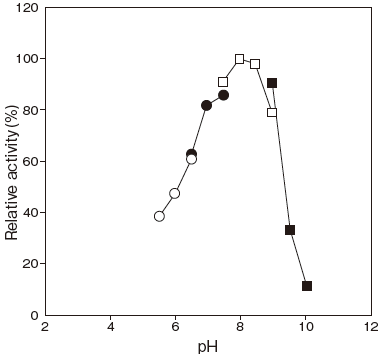
●: PIPES buffer
□: Tris-HCI buffer
■: Glycine-NaOH buffer
Fig.2 pH Stability
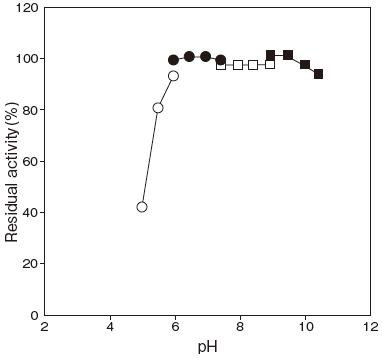
〇: Acetate buffer
●: Phosphate buffer
□: Tris-HCI buffer
■: Glycine-NaOH buffer
Fig.3 Optimum Temperature
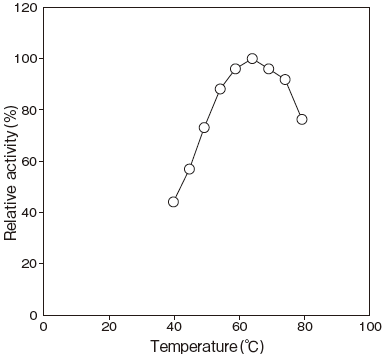
100mM Tris-HCI buffer
Fig.4 Thermal Stability
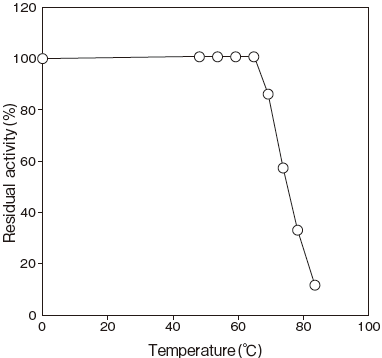
100mM Tris-HCI buffer
Assay
Principle
The assay is based on the increase in absorbance at 340nm as the formation of NADH proceeds in the following reactions:
| PNPL Ⅱ | ||
| Inorganic phosphate+Inosine | → | Hypoxanthine+D–Ribose 1–phosphate |
| XDH Ⅱ | ||
| Hypoxanthine+NAD+ | → | Xanthine+NADH+H+ |
| XDH Ⅱ | ||
| Xanthine+NAD++H2O | → | Urate+NADH+H+ |
XDH Ⅱ: Xanthine dehydrogenase
NAD : Nicotineamido adenine dinucleotide
Unit definition
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme which converts 1 μmole of inosine to hypoxanthine per minute at 37℃ under the conditions specified in the assay procedure.
Reagents
- Reaction mixture
0.2 M Tris–HCl buffer pH 8.2 1.50 ml
10 mM NAD solution 0.45 ml 30 mM KH2PO4solution 0.30 ml 20 mM Inosine solution 0.60 ml 80 U/ml XDH Ⅱ solution 1) 0.03 ml Distilled water 0.12 ml 1) : 80 U/ml XDH Ⅱ solution
Dissolve 800 U of XDH Ⅱ with 10 ml of 20 mM Tris–HCl buffer pH 8.0 containing 5 mM EDTA.- Enzyme dilution buffer
20 mM Tris–HCl buffer pH 7.5 - Reagents
NAD: NACALAI TESQUE, INC. #24334–84
Inosine: FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation#099–00231EDTA: ( 2 Na・2 H2O) KISHIDA CHEMICAL Co., Ltd.#060–29133XDH Ⅱ : Nagase Diagnostics Co., Ltd. #T–134
EDTA: Ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid
Enzyme solution
Dilute accurately 0.5 ml of the sample with enzyme dilution buffer to make a 50–fold solution. Dilute with enzyme dilution buffer to adjust the concentration as required.
Procedure
- Pipette accurately 3.0 ml of reaction mixture into a small test tube and preincubate at 37℃.
- After 5 min, add 50 μl of enzyme solution and mix to start the reaction at 37℃.
※ In the case of a test blank, add 50 μl of enzyme dilution buffer in place of enzyme solution. - After starting the reaction, measure the rate of increase per minute in absorbance at 340 nm. The rate must be measured within the linear portion of the absorbance curve.
△A/min = (As/min-Ab/min) ≦ 0.045 Abs/minAbsorbance sample : As/min blank : Ab/min
Calculation
Activity (U/ml) = {(△A/min) /(6.22×2)}× 3.05/0.05 × D6.22 : millimolar extinction coefficient of NADH at 340 nm ( cm2 /μmole)2 : a multiplier derived from the fact that 1 mole of inorganic phosphate produces 2 mole of NADH. 3.05 : final volume (ml) 0.05 : volume of enzyme solution (ml) D : times of dilution in enzyme solution
Storage
Storage at -20℃ in the presence of a desiccant is recommended.
PNPL Ⅱ活性測定法 (Japanese)
試薬液
- 反応試薬混合液
0.2M トリス–HCl 緩衝液 pH8.2 1.50 ml 10mM NAD 溶液 0.45 ml 30mM リン酸一カリ溶液 0.30 ml 20mM イノシン溶液 0.60 ml 80U/ml XDH Ⅱ溶液1) 0.03 ml 精製水 0.12 ml 1) : 80U/ml XDH Ⅱ溶液
XDH Ⅱ 800 単位 (U) を5mM EDTA を含む20mM トリス–HCl 緩衝液pH8.0 10ml で溶解する。 - 酵素溶解希釈用液
20mM トリス–HCl 緩衝液 pH7.5 - 試薬
NAD (ニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチド)
:ナカライテスク製 #24334–84
イノシン (Inosine) :富士フイルム和光純薬製 #099–00231EDTA (エチレンジアミン四酢酸・2Na・2H2O) :キシダ化学製 #060–29133XDH Ⅱ (キサンチン脱水素酵素) :ナガセダイアグノスティックス製 #T–134
酵素試料液
- 検品0.5ml を酵素溶解希釈用液で50 倍に希釈する。
- その液を酵素溶解希釈用液で適宜希釈する。
測定操作法
- 小試験管に反応試薬混合液3.0ml を正確に分注して37℃で予備加温する。
- 5 分経過後、酵素試料液50 μl を加えて混和し、37℃で反応を開始する。
※ 盲検は酵素試料液の代わりに酵素溶解希釈用液50 μl を加える。 - 反応開始後、340nm における吸光度を測定して直線的に反応している1 分間当たりの吸光度変化を求める。
求められた吸光度変化を試料液はAs/min、盲検液はAb/min とする。
ΔA/min = (As/min-Ab/min) ≦ 0.045 Abs/min
計算
活性 (U/mg) = {(ΔA/min)/ (6.22 × 2)}×3.05/0.05×D| 6.22 : | NADH の340nm におけるミリモル分子吸光係数 (cm2 / μmole) |
| 2 : | 無機リン1 モルからNADH 2モルが生成することによる係数 |
| 3.05 : | 反応総液量 (ml) |
| 0.05 : | 反応に供した酵素試料液量 (ml) |
| D : | 酵素試料液の希釈倍率 |
