LIPASE [LPBP]
from Microorganism
(Triacylglycerol acylhydrolase, EC 3.1.1.3)
(Triacylglycerol lipase)
Triglyceride + 3H2O → Glycerol + 3 Fatty Acid
| ★ | Advantages | |
| ① | Low adsorption onto cuvette | |
| ② | Stability in solution | |
Preparation and Specification
- Appearance
- : White to light brownish amorphous powder, lyophilized
- Specific activity
- : More than 800 U/mg solid
Properties
- Substrate specificity
- : See Table 1
- Molecular weight
- : 55 kDa (SDS–PAGE)
- Isoelectric point
- : pH 4.9±0.2
- Optimum pH
- : 4.2Figure 1
- pH stability
- : pH 3.5–7.0 (45℃, 60 min) Figure 2
- Optimum temperature
- : 37℃ (Phosphate buffer) Figure3
- Thermal stability
- : Stable at 37℃ and below (pH 7.5, 30 min) Figure4
- Effect of metal ions
- : See Table 2
- Low adsorption
- : See Figure 5
- Liquid stability
- : See Figure 6
- High reactivity after
long storage - : See Figure 7
- Effect of various
chemicals - : See Table 3
- Effect of detergents
- : See Table 4
Applications for Diagnostic Test
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of triglyceride.
| LPBP | ||
| TG + 3H2O | → | Glycerol + 3 Fatty acid |
| GKZ | ||
| Glycerol + ATP | → | G - 3 - P + ADP |
| GPOSP | ||
| G -3 - P + O2 | → | DHAP + H2O2 |
| POD | ||
| 2H2O2 + 4-AA + Phenol | → | Quinoneimine dye + 4 H2O |
TG : Triglyceride
DHAP : Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Table 1. Substrate specificity
| Substrate | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|
| Triolein | 100 |
| Trimyristin | 14.8 |
| Trilaurin | 34.9 |
| Tricaprylin | 92.2 |
| Tricaprin | 87.1 |
| Tricaproin | 13.5 |
| Tributyrin | 38.0 |
| Triacetin | 0 |
Table 3. Effect of detergents on LPBP activity
| Substrate | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|
| None | 100 |
| Adekanol NP695 | 91.9 |
| Adekanol NP720 | 96.2 |
| Adekanol SO120 | 86.7 |
| Adekanol B795 | 88.1 |
| Triton X305 | 91.9 |
| Emulgen B66 | 87.9 |
Table 2. Efect of various chemicals on LPBP activity
| Additives | Concentration | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| None | - | 100 |
| NiCl | 1mM | 94 |
| MnCl2 | 1mM | 90 |
| (NH4)2SO4 | 1mM | 92 |
| MgCl2 | 1mM | 98 |
| ZnCl | 1mM | 100 |
| ZnSO4 | 1mM | 100 |
| Ba(CH3COO)2 | 1mM | 101 |
| CaCl2 | 1mM | 97 |
| MoSO4 | 1mM | 100 |
| CuSO4 | 0.5mM | 103 |
| CuCl2 | 0.5mM | 99 |
| FeCl3 | 1mM | 97 |
| CoCl2 | 1mM | 106 |
| Li2CO3 | 1mM | 105 |
| EDTA | 1mM | 102 |
| KCl | 100mM | 103 |
| NaCl | 100mM | 100 |
| NaN3 | 0.05% | 98 |
| NaF | 20mM | 4 |
Fig.1 pH Optimum
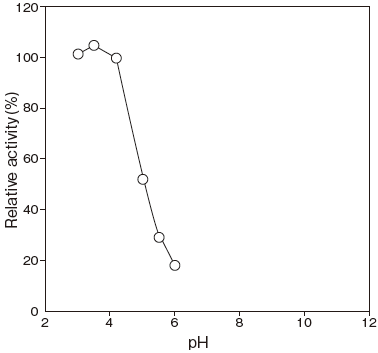
〇: Macllvaine buffer
Fig.2 pH Stability
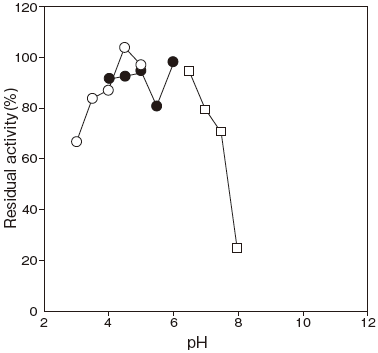
45℃, 60 min.
〇: Citrate buffer
●: 3,3-Dimethylglutarate-NaOH buffer
□: Phosphate buffer
〇: Citrate buffer
●: 3,3-Dimethylglutarate-NaOH buffer
□: Phosphate buffer
Fig.3 Optimum temperature
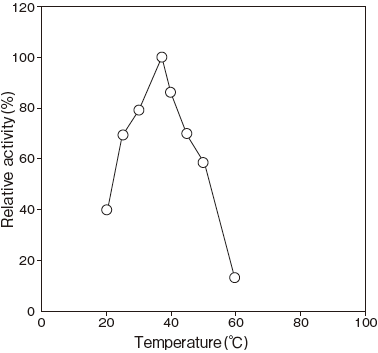
pH 6.8
40 mM Phosphate buffer
40 mM Phosphate buffer
Fig.4 Thermal Stability
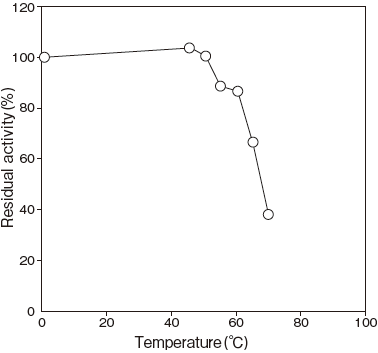
pH 7.5, 30 min.
40 mM Phosphate buffer
40 mM Phosphate buffer
Fig.5 Influence on the measurement of NEFA after TG assay demonstrating low LPBP adsorption
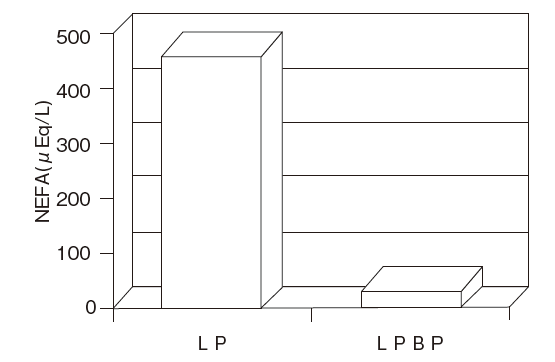
Autoanalyzer : HITACHI 7150
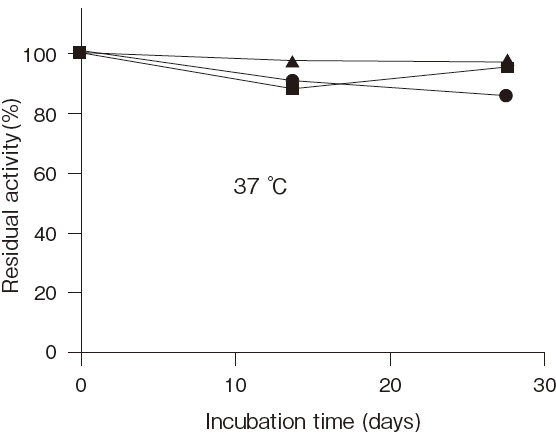
Fig.6 Stability of reconstituted LPBP
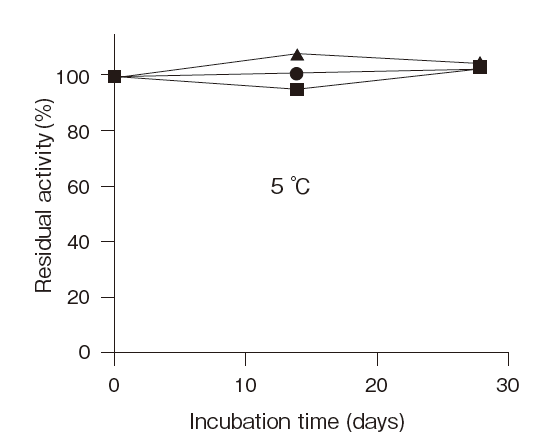
■: detergent not added
●: Adekanol B-795
▲: Adekatol SO-120
●: Adekanol B-795
▲: Adekatol SO-120
| Storage conditions : | 20mM Good’s buffer, pH 5.5 |
| 0.06% 4-amino antipyrine | |
| 0.05% NaN3, 0.05% detergent |
Fig.7 Reactivity of LPBP after long-term storage in liquid form
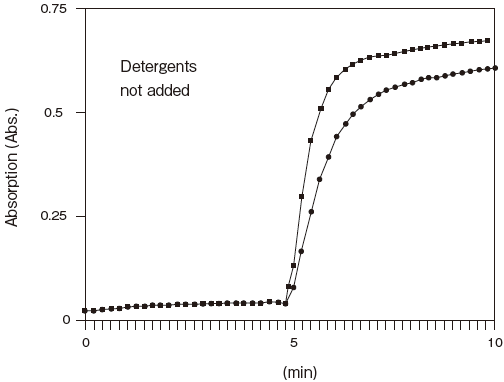
■: initial
●: at 25℃,4 weeks later
●: at 25℃,4 weeks later
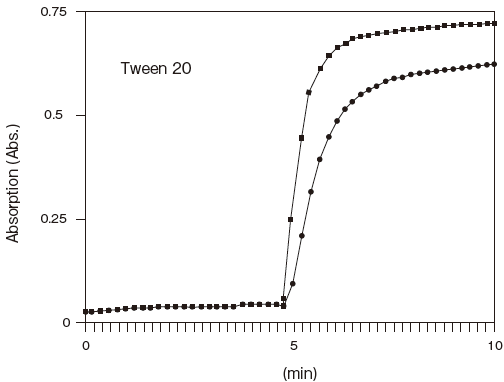
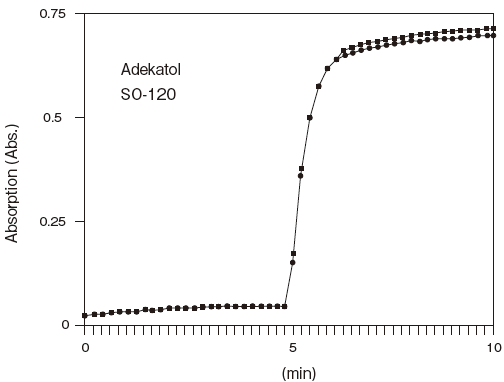
Storage conditions: 250U/ml LPBP, 0.25 U/ml MGLP
0.05% Tween 20 or Adekatol SO-120
0.05% Tween 20 or Adekatol SO-120
Assay
Principle
- The assay is based on the titration of fatty acids liberated in the following reactions:
| LPBP | ||
| Triglyceride+3 H2O | → | Glycerol+3 Fatty acid |
| ( Titration) | ||
| Fatty acid+NaOH | → | Na–Fatty acid+H2O |
Unit definition
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme which liberates 1 μmole of fatty acid per minute at 37℃ under the conditions specified in the assay procedure.
Reagents
- McIlvaine buffer pH 4.2
Mix 0.2 M Na2HPO4 and 0.1 M citrate solution and adjust pH to 4.2 at 25℃. - Substrate suspension (Olive oil and Adekatol SO–120)
50g of Olive oil (Japanese Pharmacopoeia grade and 50g of Adekatol SO–120 are suspended with 150 ml of distilled water. - Reaction stopper
Mixture of ethanol and acetone (1:1) - Indicator
1% (W/V) Phenolphthalein–ethanol solution - Titration solution
50 mM NaOH solution - Enzyme dilution buffer
0.1 M KH2PO4–NaOH buffer, pH 6.0 containing
0.1% (W/V) BSA and 0.1% (W/V) NaN3 - Reagents
Olive oil: (Japanese Pharmacopoeia grade)
Ethanol: (Japanese Pharmacopoeia grade)
Adekatol SO–120: ADEKA CORPORATION
BSA: Millipore Fraction V pH5.2 #81–053
Enzyme solution
- Accurately weigh about 10 mg of the sample and add enzyme dilution buffer to make a total 10 ml. Dilute it with enzyme dilution buffer to adjust the concentration as required.
Procedure
- Pipette accurately 5 ml of substrate suspension and 2 ml of McIlvaine buffer into test tube (24 mm i.d. × 200 mmH) and mix to preincubate at 37℃.
- After 10 min, add 0.50 ml of enzyme solution and mix to start the reaction.
※ In the case of a test blank, add 0.50 ml of enzyme dilution buffer in place of enzyme solution. - After 20 min, stop the reaction with 16 ml of reaction stopper.
- Add 3 drops of indicator and titrate the whole mixture under nitrogen gas bubbling.
※ End point of titration: Appearance of the same color as that of the blank
△V = (Vs-Vc) ≦ 1.5 mlTitration volume :Vs blank : Vc
Calculation
- Activity (U/mg of powder) = {(△V×F)/20}× 50× 1/0.5 × 1/x
20 : : reaction time (min) F : factor of titration solution (50 mM NaOH) 50 : concentration (mM) of titration solution
( 50 mM NaOH)0.5 : the volume of enzyme solution (ml) X : concentration of the sample in enzyme solution ( mg/ml)
Storage
- Storage at -20℃ in the presence of a desiccant is recommended. Enzyme activity will be retained for at least one year under this condition.
References
- Yamaguchi, T., Muroya, N., Isobe, M. and Sugiura,
M. (1973) Agric. Biol. Chem., 37, 999–1005. - Sugiura, M., Isobe, M., Muroya, N. and Yamaguchi, T. (1974) Agric. Biol. Chem., 38, 947–952.
- Sugiura, M. and Isobe, M. (1974) Biochem. Biophys.
Acta, 341, 195–200.
- Sugiura, M. and Isobe, M. (1975) Chem. Pharm. Bull., 23, 1226–1230.
- Horiuchi, Y., Koga, H. and Gocho, S. (1976) J. Biochem., 80, 367–370.
- Saiki, T., Takagi, Y. Suzuki, T., Narasaki, T., Tamura, G. and Arima, K. (1969) Agric. Biol. Chem., 33, 414.
LPBP 活性測定法 (Japanese)
試薬液
- McIlvaine 緩衝液 pH4.2
0.2M Na2HPO4 溶液と0.1M クエン酸溶液を混合してpH4.2 (25℃) に調整する。 - 基質懸濁液 (オリーブ油とアデカトールSO–120 の懸濁液)
「局方」オリーブ油50.0g とアデカトールSO–120
50.0g を精製水150ml に懸濁する。 - 反応停止液
エタノール-アセトン (1:1) 混液 - 指示液
1% (W/V) フェノールフタレン-エタノール溶液 - 滴定液
50mM NaOH 液 - 酵素溶解希釈用液
0.1% (W/V) BSA と0.1% (W/V) NaN3 を含む
0.1M KH2PO4–NaOH 緩衝液 pH6.0 - 試薬
オリーブ油:「局方」
エタノール:「局方」
アデカトールSO–120:ADEKA 製
BSA: Millipore 製 Fraction V pH5.2 #81–053
酵素試料液
- 検品約10mg を精密に量り、酵素溶解希釈用液で溶解して全容10ml とする。
その液を酵素溶解希釈用液で適宜希釈する。
測定操作法
- 試験管 (24mm i.d × 200mm H) に基質懸濁液5.0mlとMcIlvaine 緩衝液2.0ml を正確に分注して攪拌混和後、37℃で予備加温する。
- 10 分経過後、酵素試料液0.50ml を加えて混和し、37℃で反応を開始する。
※ 盲検は酵素試料液の代わりに酵素溶解希釈用液0.50ml を加える。 - 20 分経過後、反応停止液16.0ml を加えて反応を停止する。
- 指示液3 滴を加えてN2 ガスで攪拌しながら滴定液で滴定する。
ΔV = ( Vs−Vc) ≦ 1.5 ml※ 滴定の終点は盲検時と同色 (淡赤色) を呈した時点とする。
求められた滴定量を試料液はVs、盲検液はVc とする。
計算
活性 (U/mg) = {(ΔV×F)/20}×50 × 1/0.5 × 1/x| 20 : | 反応時間 (min) |
| F : | 滴定液 (50mM NaOH) のFactor |
| 50 : | 滴定液 (50mM NaOH) の濃度 (mM) |
| 0.5 : | 反応に供した酵素試料液量 (ml) |
| X : | 酵素試料液中の検品濃度 (mg/ml) |
