DIAPHORASE (NADH) [DIⅡ]
from Bacillus megaterium
(NADH: acceptor oxidoreductase, EC 1.6.5.2)
NADH + H+ + A → NAD+ + AH2
A : Hydrogen acceptor
Preparation and Specification
- Appearance
- : Yellow to yellow brownish lyophilized powder
- Specific activity
- : More than 70 U/mg solid
Properties
- Substrate specificity
- : See Table 1
- Molecular weight
- : 50 kDa ( SDS-PAGE) , 160 kDa (gel filtration)
- Isoelectric point
- : pH 4.2
- Michaelis constants
- : NADH 5.5 × 10-4M
- Optimum pH
- : 8.0–9.0Figure 1
- pH stability
- : 6.0–9.0 (37℃, 60 min) Figure 2
- Optimum temperatute
- : Optimum temperatuteFigure3
- Thermal stability
- : Stable at 50℃ and below (pH 8.0, 10 min) Figure4
Applications for Diagnostic Test
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of reduced NAD.
| DIⅡ | ||
| NADH + H+ + NTB | → | Formazane dye + NAD+ |
Table 1. Substrate specificity
| Substrate | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|
| NADH | 100 |
| NADPH | 16 |
Fig.1 pH Optimum
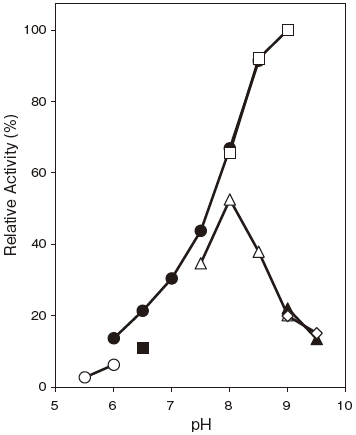
〇: Acetate buffer
●: Phosphate buffer
□: TAPS buffer
■: MES-NaOH buffer
△: Tris-HCl buffer
▲: Carbonate buffer
◇: Glycine-NaOH buffer
●: Phosphate buffer
□: TAPS buffer
■: MES-NaOH buffer
△: Tris-HCl buffer
▲: Carbonate buffer
◇: Glycine-NaOH buffer
Fig.2 pH Stability
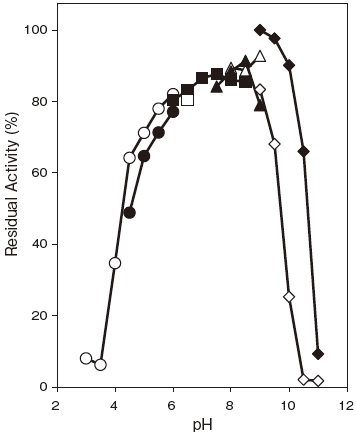
37℃, 60 min.
〇: Citrate buffer
●: Acetate buffer
□: MES-NaOH buffer
■: Phosphate buffer
△: TAPS buffer
▲: TAPS buffer
◇: Carbonate buffer
◆: Glycine-NaOH buffer
〇: Citrate buffer
●: Acetate buffer
□: MES-NaOH buffer
■: Phosphate buffer
△: TAPS buffer
▲: TAPS buffer
◇: Carbonate buffer
◆: Glycine-NaOH buffer
Fig.3 Optimum Temperature
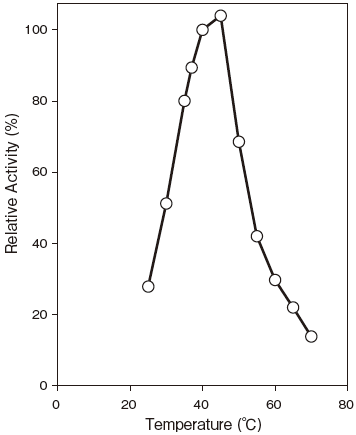
pH 8.0
100 mM Phosphate buffer
100 mM Phosphate buffer
Fig.4 Thermal Stability
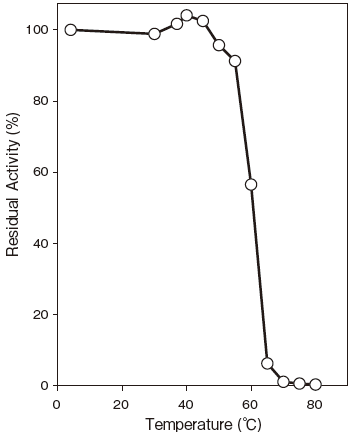
pH 8.0, 10 min
100 mM Phosphate buffer
100 mM Phosphate buffer
Assay
Principle
The assay is based on the increase in absorbance at 550 nm as the formation of formazane dye (NTBH2) proceeds in the following reaction:
| DI Ⅱ | ||
| NADH+H++NTB | → | NAD++Formazane dye |
NADH:Nicotineamido adenine dinucleotide
NTB:Nitrotetrazolium blue
Unit definition
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme which oxidizes 1 μmole of NADH to NAD+ per minute at 37℃ under the conditions specified in the assay procedure.
Reagents
- Reaction mixture
0.2 M KH2PO4–NaOH buffer
pH 8.00.50 ml 0.25% (W/V) NTB solution 0.10 ml 1% (W/V) BSA solution 0.10 ml 10 mM NADH solution 0.10 ml Distilled water 0.20 ml - Reaction stopper
0.1 N HCl solution - Enzyme dilution buffer
0.1 M KH2PO4–NaOH buffer pH8.0 containing 0.1%(w/v) BSA - Reagents
NTB: Dojindo Laboratories # 344–02033
BSA: Millipore Fraction V pH5.2 #81–053
NADH (2Na・3H2O・reduced form) :Kyowa Hakko Co. Ltd.
Enzyme solution
- Accurately weigh about 20 mg of the sample and add enzyme dilution buffer to make a total of 20 ml. Dilute it with enzyme dilution buffer to adjust the concentration as required.
Procedure
- Pipette accurately 1.0 ml of reaction mixture into a small test tube and preincubate at 37℃.
- After 5 min, add exactly 100 μl of enzyme solution and mix to start the reaction at 37℃.
※ In the case of a test blank, add 100 μl of enzyme dilution buffer in place of enzyme solution. - At 10 min after starting the reaction, add 2.0 ml of the reaction stopper to stop the reaction.
- Measure the absorbance at 550 nm.
△ A = (As−Ab) ≦ 0.370 AbsAbsorbance sample : As blank : Ab
Calculation
- Activity (U/mg of powder) = {(△A/10)/12.4} × 3.10/0.10 × 1/x
12.4 : millimolar extinction coefficient of Formazane dye at 550 nm (cm2/ μmole)10 : reaction time (min) 3.10 : final volume (ml) 0.10 : volume of enzyme solution (ml) X : concentration of the sample in enzyme solution (mg/ml)
Storage
Storage at − 20℃ in the presence of a desiccant is recommended. Enzyme activity will be retained for at least one year under this condition.
References
- Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L. and Randall, R. J. (1951) J. Biol. Chem., 193, 265–275.
- Gerlo, E. and Charlier, J. (1975) Eur. J. Biochem., 57, 40–467.
- Jablonski, E. and DeLuca, M. (1977) Biochemistry, 16, 2932–2936.
- Watanabe, H. and Hastings, J. W. (1982) Mol. Cell.
Biochem., 44, 181–187.
DI Ⅱ活性測定法 (Japanese)
試薬液
- 反応試薬混合液
0.2M KH2PO4–NaOH 緩衝液pH8.0 0.50 ml 0.25% (W/V) NTB 溶液 0.10 ml 1% (W/V) BSA 溶液 0.10 ml 10mM NADH 溶液 0.10 ml 精製水 0.20 ml - 反応停止液
0.1N HCl 液 - 酵素溶解希釈用液
0.1% (W/V) BSA を含む0.1M KH2PO4–NaOH 緩衝液 pH8.0 - 試薬
NTB (ニトロテトラゾリウムブルー) :同仁化学製 #344–02033
BSA: Millipore 製 Fraction V pH5.2 #81–053
NADH (2Na・3H2O・還元型) :協和発酵製
酵素試料液
- 検品約20mg を精密に量り、酵素溶解希釈用液に溶解して全容20ml とする。
その液を酵素溶解希釈用液で適宜希釈する。
測定操作法
- 小試験管に反応試薬混合液1.0ml を正確に分注し、37℃で予備加温する。
- 5 分経過後、酵素試料液100 μl を正確に加えて混和し、37℃で反応を開始する。
※ 盲検は酵素試料液の代わりに酵素溶解希釈用液100 μl を加える。 - 10 分経過後、反応停止液2.0ml を正確に加えて混和し、反応を停止させる。
- 550nm における吸光度を測定する。
求められた吸光度を試料液はAs、盲検液はAb とする。
ΔA = (As-Ab) ≦ 0.370 Abs
計算
活性 (U/mg) = {(△ A/10)/12.4} × 3.10/0.10 × 1/x| 12.4 : | NTBH2 の550nm におけるミリモル分子吸光係数 (cm2/ μmole) |
| 10 : | 反応時間 (min) |
| 3.10 : | 反応総液量 (ml) |
| 0.10 : | 反応に供した酵素試料液量 (ml) |
| X : | 酵素試料液中の検品濃度 (mg/ml) |
