BILIRUBIN OXIDASE [BODⅡ]
from Bacillus subtilis
(bilirubin : oxygen oxidoreductase, EC 1.3.3.5)
2 bilirubin + O2 → 2 biliverdin + 2H2O
Preparation and Specification
- Appearance
- : Light blue to blue powder
- Specific activity
- : More than 5.0U/mg
Properties
- Molecular weight
- : 63 kDa (SDS–PAGE)
46 kDa (Superdex 200)
- Isoelectric point
- : 4.6
- Optimum pH
- : 7.0-8.0 (Bilirubin F)Figure 1
- : 5.5-6.0 (Bilirubin C)Figure 2
- : 4.5-5.0 (Ditaurobilirubin)Figure 3
- : 4.5-5.0 (ABTS)Figure 4
- pH stability
- : 4.5-11.0 (37 °C, 60 min.)Figure 5
- Optimum temperature
- : 55-65 °C (pH4.5, Citrate buffer, ABTS)Figure 6
- Thermal stability
- : Stable at 80 °C and below (pH 7.0, 30 min.)Figure 7
- Effect of metal ions
- : See Table 1
- Effect of detergents
- : See Table 2
Applications for Diagnostic Test
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of bilirubin or ditaurobilirubin.
| BODⅡ | ||
| 2 bilirubin + O2 | → | 2 biliverdin + 2 H2O |
Table 1. Effect of metal ion on BODⅡ activity (ABTS)
| Metal ion | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|
| None | 100 |
| 1mM NiCl2 | 90 |
| 1mM BaCl2 | 91 |
| 1mM MnCl2 | 84 |
| 1mM CuCl2 | 97 |
| 1mM ZnCl2 | 89 |
| 1mM CoCl2 | 88 |
| 1mM MgCl2 | 86 |
| 1mM CaCl2 | 92 |
| 1mM Ba(CH3COO)2 | 104 |
| 1mM FeCl3 | 0 |
| 1mM FeSO4 | 0 |
| 1mM LiCl2 | 98 |
| 1mM NH4Cl | 98 |
| 1mM ZnSO4 | 101 |
| 1mM NaN3 | 14 |
| 10mM KCl | 13 |
| 0.1M NaCl | 17 |
| 1mM EDTA | 91 |
Table 2. Effect of detergents on BOD Ⅱ activity (ABTS)
| Detergent (0.1%) | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|
| None | 100 |
| Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) | 67 |
| Tween 80 | 99 |
| Adekatol PC-8 | 106 |
| NP-690 | 74 |
| LO-7 | 86 |
| Nikkol MYL-10 | 104 |
| Cetylpyridinium chloride | 75 |
| Sodium laurylbenzene sulfonate | 2 |
| Cholic acid | 86 |
Fig.1 pH Optimum (Bilirubin F)
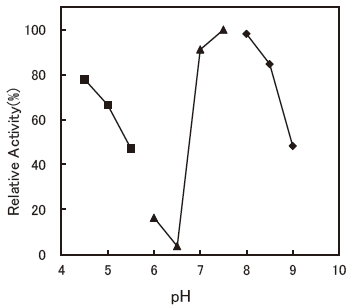
▲: Phosphate buffer
●: Tris-HCl buffer
Fig.2 pH Optimum (Bilirubin C)
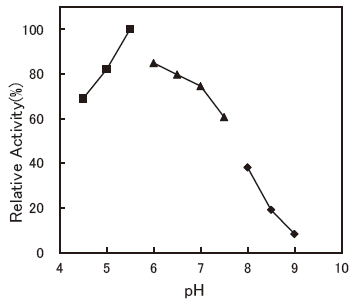
▲: Phosphate buffer
●: Tris-HCl buffer
Fig.3 pH Optimum (Ditaurobilirubin)
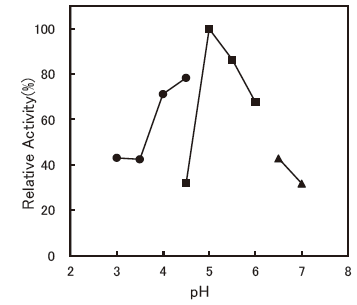
■: Acetate buffer
▲: Phosphate buffer
Fig.4 pH Optimum (ABTS)
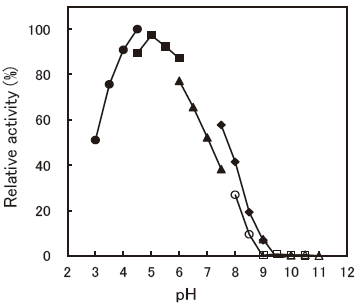
■: Acetate buffer
▲: Phosphate buffer
◆: Tris-HCl buffer
〇: TAPS buffer
□: Carbonate buffer
△: Glycine-NaOH buffer
Fig.5 pH Stability (ABTS)
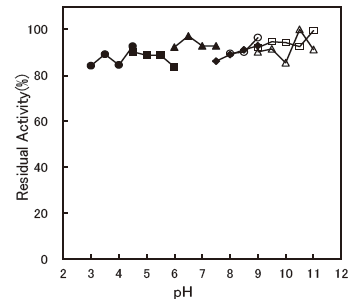
●: Citrate buffer
■: Acetate buffer
▲: Phosphate buffer
◆: Tris-HCl buffer
〇: TAPS buffer
□: Carbonate buffer
△: Glycine-NaOH buffer
Fig.6 Optimum Temperature (ABTS)
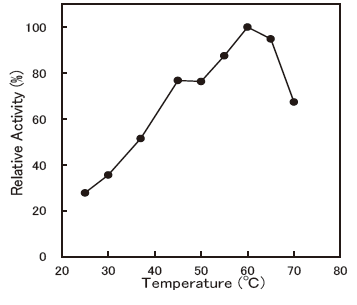
0.1M Citrate Buffer
Fig.7 Thermal Stability (ABTS)
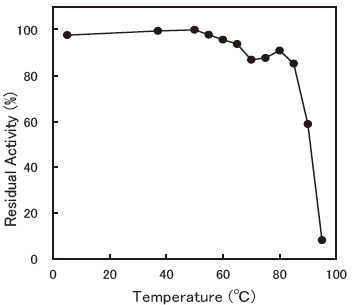
50mM Phosphate Buffer
Assay
Principle
The assay is based on the increase in absorbance at 405 nm as the formation of in the following reaction:
| BODⅡ | ||
| ABTS+O2 | → | OxidizedABTS+H2O |
ABTS : (2,2'-Azino-bi (s 3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid))
Unit definition
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme, which converts 1 μmole of oxidABTS per minute 37℃ under the conditions specified in the assay procedure.
Reagents
- Reaction mixture
Dissolve 274 mg of ABTS with 0.1 M Citric acid-trisodium
Citrate Dihydrate pH 4.5 to make a total of 100 ml - Enzyme dilution buffer
10 mM Tris-HCl buffer, pH 8.5 containing 0.05 % (W/V) BSA - Reagent
Citric acid・H2O:FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical CorporationTris (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane :
Special grade #035–03495Sigma-Aldrich Co. #T1503Trisodium Citrate Dihydrate:FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical CorporationABTS (2,2'–Azino–bis (3–ethylbenzothiazoline–6–sulfonic acid) : Sigma Chemical Co. #A1888
Special grade #191–01785
BSA: Millipore Co. Fraction V pH5.2
Enzyme solution
Accurately weigh about 20 mg of the sample and add enzyme dilution buffer to make a total of 20 ml. Dilute it with enzyme dilution buffer to adjust the concentration to within 0.05 U/ml.
Procedure
- Pipette accurately 1.0 ml of reaction mixture into a small test tube and preincubate at 37℃.
- After 5min, add 20 μl of enzyme solution and mix to start the reaction at 37°C.
※ In the case of a test blank, add 20 μl of enzyme dilution buffer in place of enzyme solution. - After starting the reaction, measure the rate of increase per minutes in absorbance at 405 nm. The rate must be measured within the linear portion of the absorbance curve.
△A/min = As/min- Ab/min ≦ 0.20 AbsAbsorbance sample : As/min blank : Ab/min
Calculation
Activity (U/mg) = {(△A/min)/(36 × 3)} × 1.02/0.02 × 1/x| 36 : | millimolar extinction coefficient of ABTS at 405 nm (cm2 /μmol) |
| 3 : | Coefficient of transformation when substrate is bilirubin. |
| 1.02 : | final volume (ml) |
| 0.02 : | volume of enzyme solution (ml) |
| X : | concentration of the sample in enzyme solution (mg/ml) |
Storage
Storage at−20°C in the presence of a desiccant is recommended.
References
- Sakasegawa, S., Ishikawa, H., Imamura,S., Sakuraba, H., Goda S., and Ohshima T. ( 2006) Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 72, 972.
BODⅡ活性測定法 (Japanese)
試薬液
- 0.1M クエン酸-クエン酸Na pH4.5
クエン酸21.0g を精製水で全容 1L とする。クエン酸Na 29.4g を精製水で全容 1L とする。
クエン酸溶液とクエン酸Na 溶液を混合して、pHを4.5 (25℃) に調製する。 - 試薬混合液
ABTS 274mg を0.1M クエン酸-クエン酸Na pH4.5 で溶解し、全容 100ml とする。 - 酵素溶解希釈用液 (0.05% BSA を含む 10mM トリス -HCl 緩衝液 pH8.5)
BSA 0.50g を10mM トリス-HCl 緩衝液 pH8.5 で溶解し、全容 1L とする。 - 試薬リスト
クエン酸 (Citric acid・H2O) :富士フイルム和光純薬製 特級 #035–03495クエン酸三ナトリウム二水和物 (Trisodium Citrate
Dihydrate) :富士フイルム和光純薬製 特級 #191–01785トリス (ヒドロキシメチル) アミノメタン:シグマ製 # T1503ABTS (2,2'–Azino–bis (3–ethylbenzothiazoline–6–
sulfonic acid) :シグマ製 #A1888
BSA: Millipore 製 Fr V, pH5.2 #81-053
酵素試料液
- 検品約 20mg を精密に量り、酵素溶解希釈用液で溶解して全容 20ml とする。その液を酵素溶解希釈用液で0.05U/ml 濃度となるように適宜希釈する。
測定操作法
- 石英セルに試薬液を 1.0ml ずつ正確に分注して37℃で予備加温する。
- 5 分経過後、酵素試料液 20 μl を正確に加えて混和し、37℃で反応を開始する。
※ 盲検は酵素試料液の代わりに酵素溶解希釈用液 20μl を加える。 - 反応開始後、405 nm における吸光度を測定して、3分目から5 分目の1 分間当たりの吸光度変化を求める。
求められた吸光度変化を
試料液については As/min
盲検液については Ab/min とする。
△A/min=As/min -Ab/min ≦0.20Abs.
計算
- 活性 (U/mg) = {(△ A/min)/(36 × 3)} × 1.02/0.02 × 1/x
36 : ABTS のミリモル分子吸光係数 (cm2/ μmole)3 : 基質をビリルビンにした値に合わせる為の係数 1.02 : 反応総液量 (ml) 0.02 : 反応に供した酵素試料液量 (ml) X : 酵素試料液中の検品濃度 (mg/ml)
注意点
- 本来の基質であるビリルビンを基質として活性測定が困難なので、ABTS を基質として活性測定し、ビリルビンを基質として活性値に合うように係数で調整した。
- 試薬混合液に使用の0.1M クエン酸- クエン酸Na pH4.5 について調製後の保存期間により活性値の上昇が認められたため用時調整とする。
