HEXOKINASE [HKⅢ]
from Rhodothermus obamensis
(ATP:D–hexose–6–phosphotransferase, EC 2.7.1.1)
D–Glucose + ATP → D–Glucose–6–phosphate + ADP
Preparation and Specification
- Appearance
- : White to light grayish lyophilized powder
- Specific activity
- : More than 100 U/mg solid
Properties
- Substrate specificity
- : See Table 1
- Molecular weight
- : 140 kDa (gel filtration)
- Isoelectric point
- : pH 5.64
- Michaelis constants
- : Glucose 0.46 mM
ATP 0.21 mM
- Optimum pH
- : 7.5–8.0Figure 1
- pH stability
- : 5–10Figure 2
- Thermal stability
- : Stable at 75℃ and below (pH8.5, 10 min) Figure3
Applications for Diagnostic Test
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of glucose or creatine kinase activity when coupled with glucose–6–phosphate dehydrogenase (T-51).
| HK Ⅲ | ||
| D-Glucose + ATP | → | D-Glucose-6-phosphate + ADP |
| G6PDHⅡ | ||
| D-Glucose-6-phosphate + NADP+ | → | |
| D-Glucono-δ-lactone-6-phosphate+NADPH+H+ | ||
Table 1. Substrate specificity
| Substrate | Relative activity (%) |
|---|---|
| Glucose | 100 |
| Mannose | 27 |
| Glucosamine | 66 |
| 2-deoxy-D-glucose | 37 |
| Galactose | 11 |
| 1,5-AG | 3 |
| Fructose | 0 |
| Sorbitol | 0 |
| Saccharose | 0 |
Fig.1 pH Optimum
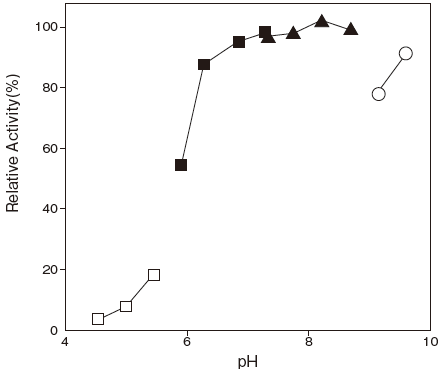
▲: Phosphate buffer
■: Tris-HCI buffer
〇: Glycine-NaOH buffer
Fig.2 pH Stability
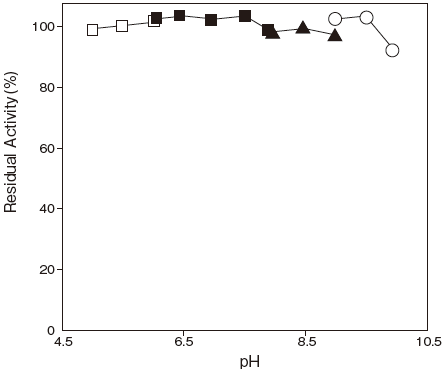
□: Acetate buffer
■: Phosphate buffer
▲: Tris-HCI buffer
〇: Glycine-NaOH buffer
Fig.3 Thermal Stability
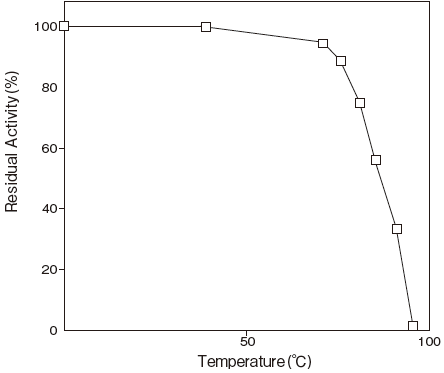
Tris-HCI buffer
Assay
Principle
The assay is based on the increase in absorbance at 340 nm as the formation of NADPH proceeds in the following reactions:
| HK Ⅱ | ||
| D–Glucose+ATP | → | Glucose–6–phosphate+ADP |
| G6PDH Ⅱ | ||
| Glucose–6–phosphate+NADP+ | → | |
| D–Glucono–δ–lactone–6–phosphate + NADPH + H+ | ||
ATP:Adenosine triphosphate
NADP:Nicotineamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
G6PDH Ⅱ:Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
Unit definition
One unit is defined as the amount of enzyme which generates 1 μmole of NADPH per minute at 37ºC under the conditions specified in the assay procedure.
Reagents
- Reaction mixture
0.2 M Tris-HCl buffer pH 8.0 0.6 ml 0.1 M Glucose solution 0.3 ml 40 mM ATP solution pH 7.0 0.3 ml 100 U/ml G6PDH Ⅱ solution1) 0.3 ml 10 mM NADP solution 0.3 ml 0.1 M MgCl2solution 0.3 ml Distilled water 0.9 ml 1) : 100 U/ml G6PDH Ⅱ solution
Disolve 1,000 U of G6PDH with 10 ml of 10 mM
Tris–HCl buffer pH 8.0. - Enzyme dilution buffer
0.1M KH2PO4–NaOH buffer pH 7.0 containing 0.1 % ( W/V) BSA and 0.1 % (W/V) Triton X–100. - Reagents
Triton X–100: The Dow Chemical Company
NADP (oxidized form) :FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical CorporationG6PDH Ⅱ : Nagase Diagnostics Co., Ltd. # T–51
# 308–50463
ATP (2Na・3H2O) : Kyowa Hakko Co., Ltd.
BSA: Millipore Fraction V pH 5.2 # 81–053
Enzyme solution
Accurately weigh about 20 mg of the sample and add enzyme dilution buffer to make a total of 20 ml. Dilute it with enzyme dilution buffer to adjust the concentration as required.
Procedure
- Pipette accurately 3.0 ml of reaction mixture into a small test tube and preincubate at 37℃.
- After 5 min, add exactly 50 μl of enzyme solution and mix to start the reaction at 37℃.
※ In the case of a test blank, add 50 μl of enzyme dilution buffer in place of enzyme solution. - After starting the reaction, measure the rate of increase per minute in absorbance at 340 nm. The rate must be measured within the linear portion of the absorbance curve.
△A/min = (As/min-Ab/min) ≦ 0.030 Abs/minAbsorbance sample : As/min blank : Ab/min
Calculation
- Activity (U/mg of powder) = {(△A/min)/6.22} × 3.05/0.05 × 1/x
6.22: millimolar extinction coefficient of NADPH at 340 nm ( cm2 /μmole)3.05 : final volume (ml) 0.05 : volume of enzyme solution (ml) X : concentration of the sample in enzyme solution ( mg/ml)
Storage
Storage at -20℃ in the presence of a desiccant is recommended.
References
- Colowick, S. P. (1973) The Enzymes (3rd Ed.) , 4, 1–48.
- Barnard, E. A. (1975) Methods Enzymol., 42, 6–25.
- Wright, C. L. and Warsy, A. S. (1978) Biochem. J., 175, 125–135.
- Li SJ, Umena Y, Matsvoka T, Kita A, Fukui K, and
Morimoto Y. (2007) Biochem. Biophys. Res. commun., 358, 1002–1007.
HK Ⅱ活性測定法 (Japanese)
試薬液
- 反応試薬混合液
0.2M トリス–HCl 緩衝液 pH8.0 0.6 ml 0.1M グルコース溶液 0.3 ml 40mM ATP 溶液 pH7.0 0.3 ml 100U/ml G6PDH Ⅱ溶液1) 0.3 ml 10mM NADP 溶液 0.3 ml 0.1M 塩化マグネシウム溶液 0.3 ml 精製水 0.9 ml 1) : 100U/ml G6PDH Ⅱ溶液
G6PDHⅡ 1,000 単位 (U) を10mM トリス–HCl
緩衝液pH8.0 10ml で溶解する。 - 酵素溶解希釈用液
0.1% (W/V) BSA と 0.1% (W/V) トリトンX–100を含む 0.1M KH2PO4–NaOH 緩衝液 pH7.0 - 試薬
トリトンX–100:Dow Chemical 製
NADP (ニコチンアミドアデニンジヌクレオチド・リン酸酸化型) :富士フイルム和光純薬製 #308–50463G6PDH Ⅱ (グルコース–6–リン酸脱水素酵素) :ナガセダイアグノスティックス製 #T–51ATP (アデノシン三リン酸・2Na・3H2O) :協和発酵製BSA:Millipore 製 Fraction V pH5.2 #81–053
酵素試料液
- 検品約 20mg を精密に量り、酵素溶解希釈用液で溶解して全溶 20ml とする。
その液を酵素溶解希釈用液で適宜希釈する。
測定操作法
- 小試験管に反応試薬混合液 3.0ml を正確に分注し、37ºC で予備加温する。
- 5 分経過後、酵素試料液 50 μl を正確に加えて混和し、37ºC で反応を開始する。
※ 盲検は酵素試料液の代わりに酵素溶解希釈用液 50μl を加える。 - 反応開始後、340nm における吸光度を測定して直線的に反応している1 分間当たりの吸光度変化を求める。
求められた吸光度変化の試料液は As/min、盲検液は
Ab/min とする。
ΔA/min = (As/min-Ab/min) ≦ 0.030Abs/min
計算
活性 (U/mg) = {(ΔA/min)/6.22} × 3.05/0.05 × 1/x| 6.22 : | NADPH の340nm におけるミリモル分子吸光係数 (cm2 /μmole) |
| 3.05 : | 反応総液量 (ml) |
| 0.05 : | 反応に供した酵素試料液量 (ml) |
| X : | 酵素試料液中の検品濃度 (mg/ml) |
