Selective Cleaning Technology
We propose a technology that selectively cleans various combinations of metals and resins at the nano level while minimizing damage.
Selective cleaning refers to the process of making what is needed and removing what is unnecessary. For example, when
washing the face in daily life, sebum contamination should be removed while a certain amount of oil should remain.
Similarly, selective cleaning is required in the cleaning process in the industrial field. However, there is often a
trade-off between increasing the removability of specific substances (stains) and reducing damage to the base material
to which the stains are attached. The difficulty of this process increases as the variety of stains and base materials
grows.
Materials used in the manufacturing process of semiconductors, semi-metals, FPDs, etc. often produce devices with
multiple layers of different metals. The problem in this process is galvanic corrosion, in which the solubility of only
certain metals increases due to the difference in ionization tendency between the metals in contact with each
other. Selective corrosion protection is a method to suppress this galvanic corrosion. Selective residue removal removes
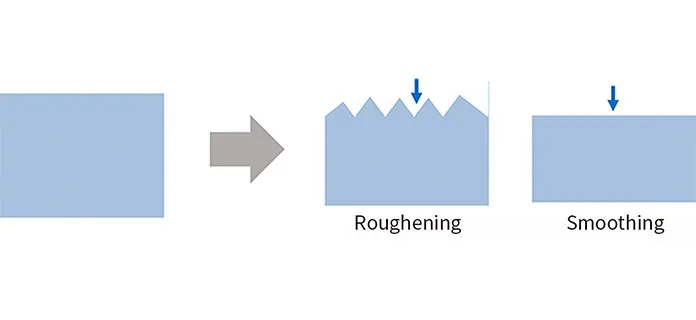
only the residue of other specific metals and polymers and does not damage others. There is also a need for etch
roughness control, which adjusts the surface roughness after the metal is etched, and constant velocity etching, which
dissolves several different metals at the same rate. Our selective cleaning technology can meet them.
Four Selective Cleaning Technologies Proposed by NAGASE



Application Example of Selective Etching Technology
Utilizing formulation technology, we have developed chemical components that prevent the dissolution of metals with different ionization tendencies, thereby suppressing galvanic corrosion.
The base metal (Mo) selectively dissolves

No galvanic corrosion

Additionally, we can suppress galvanic corrosion that occurs with various combinations of metals such as Au and Ni, and Au and Ti. For more details, please contact us.
